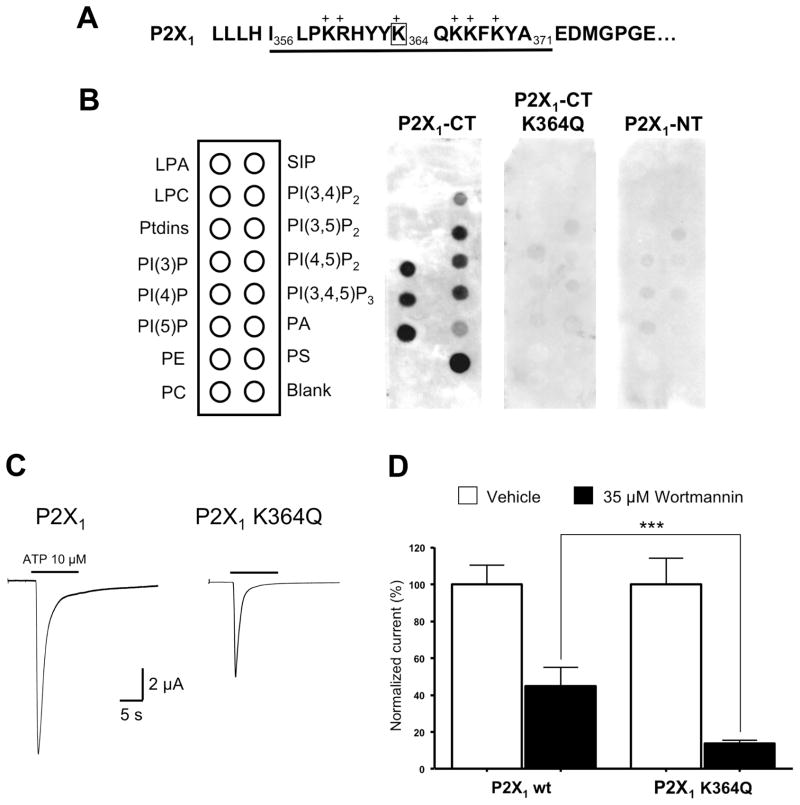
Figure 7. Lysine K364 in the proximal C-terminal domain of P2X1 subunit is a critical determinant for phosphoinositides binding and sensitivity to wortmannin.
(A) Sequence of the proximal C-terminal domain of rat P2X1 subunit. (B) The GST construct containing the proximal C-terminal domain I356-A371 of the P2X1 subunit binds to several anionic phosphoinositides, including PI(4,5)P2. Binding is suppressed when the single lysine K364 is replaced with glutamine. No binding is detected when using the GST construct containing the N-terminal domain of P2X1 (P2X1-NT) as negative control. LPA: Lysophosphatidic Acid, LPC: Lysophosphocholine, PE: Phosphatidylethanolamine, PC: Phosphatidylcholine, S1P: Sphingosine-1-phosphate, PA: Phosphatidic Acid, PS: Phosphatidylserine. (C) Representative traces showing that the mutant receptor P2X1 K364Q carries smaller ATP-evoked currents than the wild-type P2X1 receptor (n= 10, * p < 0.05). (D) The mutant receptor P2X1 K364Q is also more sensitive than the wild-type receptor to depletion of PI(4,5)P2 induced by 35 μM wortmannin (n= 9–19, *** p < 0.001).