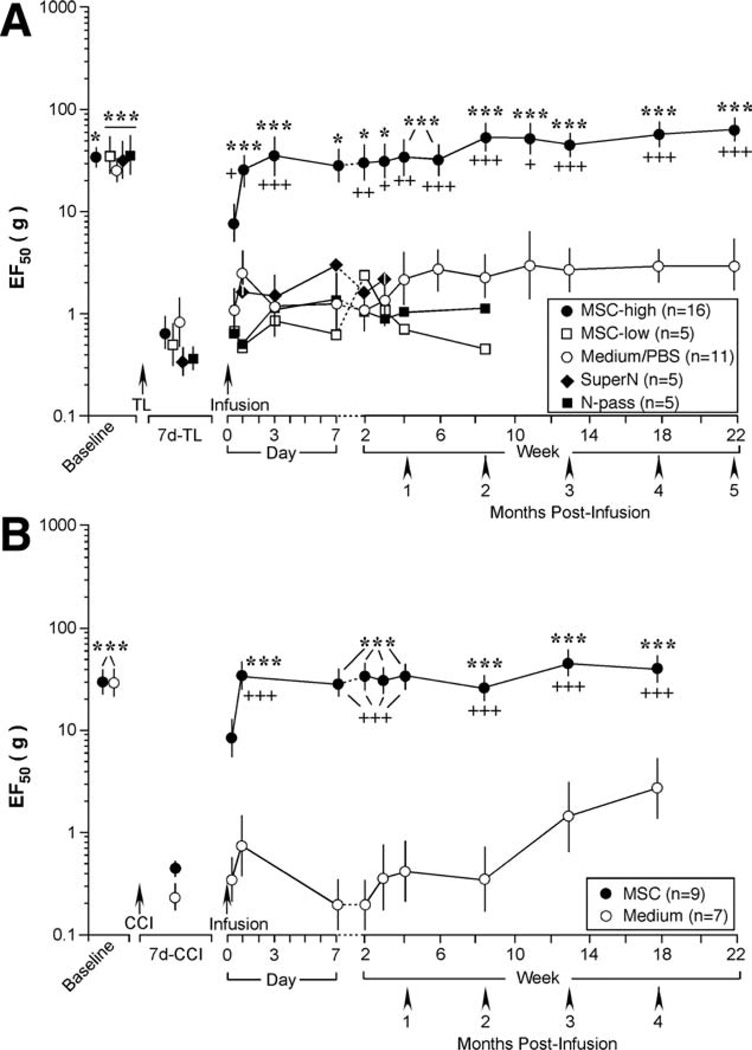
Figure 2.
Bone marrow stromal cell (BMSC) reversed pain hypersensitivity after tendon injury. (A): Cultured cells were infused through a tail vein at 0.2 ml with 1.5 × 103 (low-dose, MSC-low) or 1.5 × 106 (high-dose, MSC-high) BMSCs after 7 day-tendon ligation (TL). Control infusions were culture medium/phosphate-buffered saline, the supernatant of cell suspension (SuperN), and cells (1.5 × 106 BMSCs) after 20 passages (N-pass). When compared with low-dose BMSCs and controls, infusion of 1.5 × 106 BMSCs significantly increased EF50s from 1 day to 5 months after infusion. Asterisks denote significant differences versus 7 day-TL: *, p < .05; ***, p < .001. Cross signs denote significant differences versus medium: +, p < .05; ++, p < .01; +++, p < .001. (B): Infusion of BMSC reversed pain hypersensitivity after chronic constriction injury (CCI) of the infraorbital nerve of the rat. When compared with control (culture medium), infusion of BMSCs significantly increased EF50s from 1 day to 4 months after infusion. Asterisks denote significant differences versus 7 day-CCI: ***, p < .001. Cross signs denote significant differences versus medium: +++, p < .001. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals of EF50s. Abbreviations: CCI, chronic constriction injury; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; TL, tendon ligation.