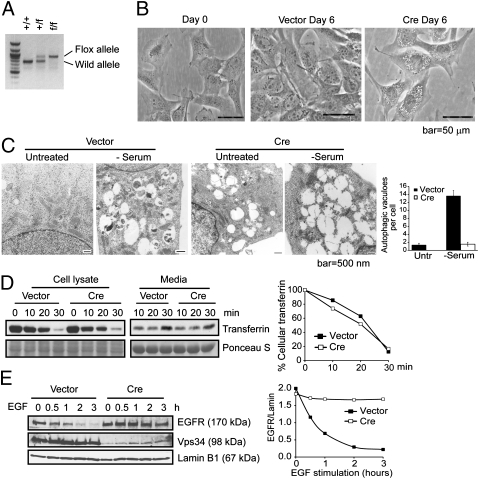
Fig. 1.
Ablation of Vps34 leads to defective autophagosome formation and endocytic protein turnover in MEFs. (A) PCR analysis with the Pik3c3-5′ and 3′ arm primers (Fig. S1) using genomic DNA isolated from MEFs generated from Vps34+/f breeding pair. (B) MEFs were observed by phase/contrast microscopy upon control or Cre infection for 6 d. Representative images are shown. (C) MEFs infected with vector control or Cre were left in full medium or serum starved for 6 h and observed by EM. Large-sized empty vacuoles are observed in Vps34-null MEFs representing single-membraned swollen endosomes/lysosomes. Serum starvation induced the appearance of autophagosomes in wild-type, but not Vps34-null MEFs. Quantification of the number of autophagosomes was obtained by counting 10–20 cells and the averages ± SEM are shown. (D and E) Endocytic EGFR degradation but not transferrin recycling is blocked in Vps34-null cells. (D) Vector control or Cre-infected MEFs were serum starved for 4 h and incubated with biotinylated-transferrin, then stripped and chased with unlabeled transferrin for the indicated times. Cells and culture media were collected and analyzed for biotinylated-transferrin levels. The relative amounts of intracellular transferrin at each time point was quantified by densitometry and normalized to that of time 0. (E) Vector control or Cre-infected MEFs were serum-starved overnight and stimulated with EGF (100 ng/mL) for the indicated times. EGFR protein level is quantified relative to Lamin B1.