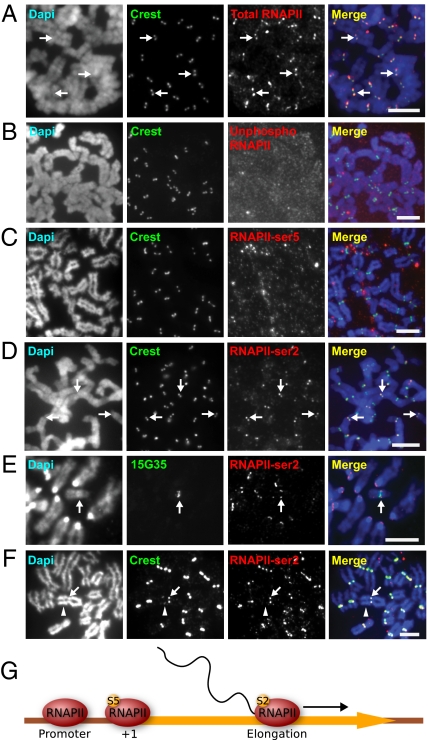
Fig. 1.
RNAPII-ser2 localizes to the mitotic kinetochore and is associated with active kinetochore activity. (A) Antibody 4H8total RNAPII immunostained the kinetochores of HeLa cells, as shown by the colocalization with CREST anti-centromere signals (arrows). (B) Antibody 8WG16unphosphorylated, specific for unphosphorylated RNAPII did not immunostain HeLa mitotic kinetochores. (C) Antibody H14phosphoSer5, which recognizes RNAPII phosphorylated at serine 5 (RNAPII-ser5) associated with transcription initiation, showed no staining of the kinetochores. (D) H5phosphoSer2, specific for elongating RNAPII, stained the kinetochores of mitotic HeLa cells (arrows). (E) Combined immunofluorescence/DNA-FISH (antibody H5phosphoSer2 and 10q25 band-specific 153G5 BAC probe) of mouse ES mardel (10) cells showed the presence of RNAPII-ser2 at the mardel (10) neocentromere (arrow) as well as at endogenous mouse kinetochores. (F) RNAPII-ser2 was present only at the active neocentromere of the PD-NC4 chromosomes (arrow) but not at the inactive native centromere (arrowhead, as indicated by the weaker CREST signals attributed to residual CENP-B). (G) Schematic depicting the change in RNAPII phosphorylation status across the transcription cycle. At the promoter, RNAPII is unphosphorylated. At transcription initiation, RNAPII is phosphorylated at serine 5 (S5), but before the RNAPII complex is competent for transcription elongation it must be phosphorylated at serine 2 (S2). (Scale bars: 5 μm.)