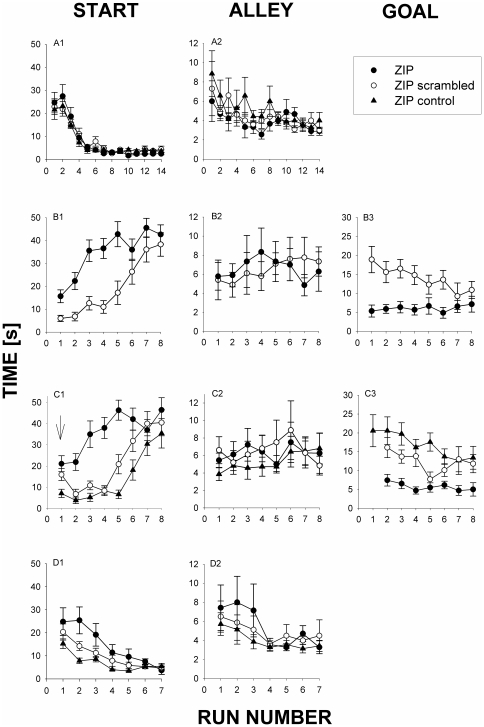
Figure 4. Inhibition of AcbC PKC/Mzeta inhibits memory reconsolidation.
Rats were trained to traverse a runway alley to obtain a remifentanil (RMF; 0.032 mg/kg iv) injection paired with a conditioned light stimulus (conditioned stimulus, CS) on day A (top row). On day B (second row), animals received either ZIP (0.5microliter of 1.5 mM; N = 9) or scrambled ZIP peptide (N = 10) within the confines of the runway (30 min prior to starting run #1) and were presented only with the CS upon traversing the runway. The ZIPcontrol group (N = 7) received ZIP in their home cage without being tested in the runway. Two days later (C), the ZIP- and the scrambled peptide groups received an injection of RMF (drug-induced reinstatement of responding) only after the first run of the day (arrow); ZIP-control animals did not receive the drug reminder; all rats were presented with the CS upon entering the goal area. The next day (D), all animals were retrained with RMF+CS. Column 1, start time; column 2; alley time; column 3, goal time (not determined on days A and D because of confounding direct sedative effects of RMF). Column 1, start time; column 2; alley time; column 3, goal time (determined in absence of RMF). Note that on days B and C, that for all animals that did not leave the start area, no alley times and goal times could not be determined. Consequently, the number of animals that contributed to the mean times shown here were, on day B, run #3, N = 10 in the scrambled peptide group, and N = 9 in the ZIP group; run #4, 10 scrambled, 9 ZIP; run #5, 10 scrambled, 6 ZIP; run #6, 10 scrambled, 8 ZIP; run #7, 7 scrambled, 8 ZIP; and run #8, 7 scrambled, 9 ZIP. On day C, the respective numbers were: run #3, 10 scrambled, 9 ZIP, 7 ZIP-control; run #4, 10 scrambled, 7 ZIP, 7 ZIP-control; run #5, 10 scrambled, 6 ZIP, 7 ZIP-control; run #6, 8 scrambled, 6 ZIP, 7 ZIP-control; run #7, 7 scrambled, 7 ZIP, 6 ZIP-control; and run #8, 6 scrambled, 4 ZIP, and 5 ZIP-control. Statistical analysis yielded the following results: Panel B1: t-student for run #1: t = 3,202 with 17 degrees of freedom. (P = 0,005). Panel B3: t-student for run #1: t = 3,423 with 17 degrees of freedom. (P = 0,003). Panel C1: 1W-ANOVA for run #2: (ranks yields the same significance) F(2,23) = 10.660 p<0.001 Posthoc (Bonferroni): ZIP vs ZIP-control p<0.001- ZIP vs ZIP-scrambled p<0.01. ZIP-scrambled vs ZIP control.NS. Panel C3, run #1: only ZIP vs ZIP-CONTROL yielded significant in post-hoc comparison.