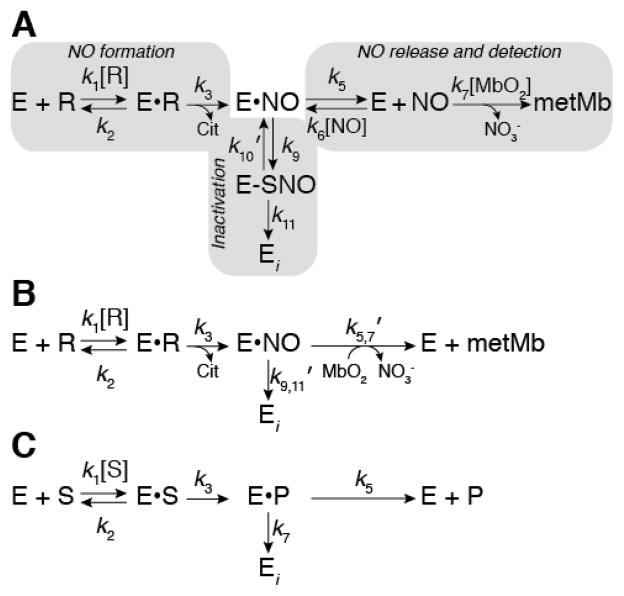
Figure 2.
Kinetic model of iNOS inactivation. (A) Complete kinetic model of iNOS auto-inactivation by S-nitrosation and dimer dissociation where the kinetic readout is reaction of NO with MbO2. Gray boxes indicate the NO formation, inactivation, and NO release/detection pathways. E represents the enzyme (i.e. iNOS), R represents arginine, E•R represents arginine bound within the iNOS active-site, E•NO represents nitric oxide sequestered within iNOS but not necessarily bound to the heme iron, E-SNO represents iNOS S-nitrosated at the Zn2+-tetrathiolate cysteines, and Ei represents inactivated iNOS. (B) A simplified kinetic model in which the inactivation and NO release/detection pathways are represented by net rate constants. (C) General kinetic model of a suicide substrate where S represents the substrate and P represents the product.