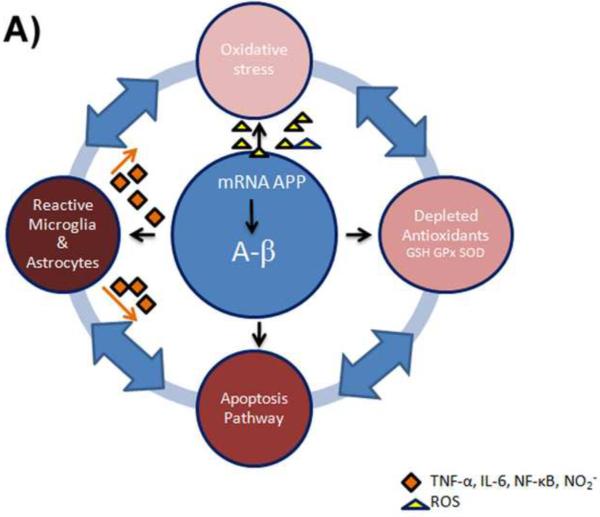
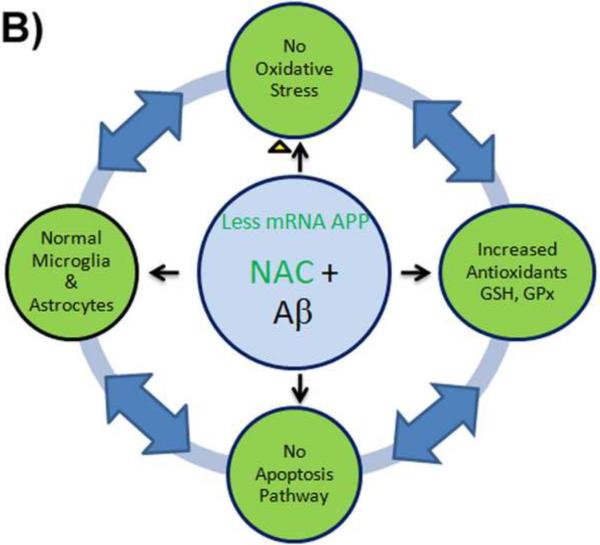
Figure 4.
A) Aβ produces ROS that eventually leads to the depletion of antioxidants and oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease. The increased oxidation induces apoptotic signaling pathways and inflammation in astrocytes. Astrocytes release toxic inflammatory mediators and free radicals, accelerating activation of microglia and neurodegeneration, connecting the cycle of negative events perpetuating AD.
B) NAC down-regulates APP gene transcription, resulting in undetectable levels of APP mRNA. Thus, since less Aβ is transcribed, fewer free radicals are produced by Aβ. NAC increases antioxidant levels of glutathione and reacts with ROS preventing oxidative stress. The decreased oxidation in the cells induces anti-apoptotic signaling pathways and prevents inflammation of the cell. NAC directly inhibits inflammatory factor NF-κB and blocks production of nitric oxide from inducible nitric oxide synthase and inflammatory cytokines.