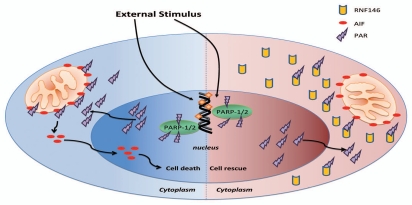
Figure 2.
Potential molecular mechanism for RNF146 induced neuroprotection against Parthanatos. Extensive extra-cellular stimulus can activate PARP-1/2 in nucleus. The activated PARP-1/2 can lead to production of large sum of PAR in nucleus. These PAR can translocated to cytoplasm where can bind with AIF in outer membrane of mitochondria (left). The binding of PAR with AIF can trigger the release of AIF from mitochondria (left). The AIF then translocates to nucleus and induces Parthanatos of cells (left). However in the presence of RNF146, the PAR will bind to RNF146 preemptively, hereby prevent the binding of PAR with AIF in mitochondria (right). The abrogation of binding between PAR and AIF by RNF146 will inhibit Parthanatos and contribute to cell rescue (right).