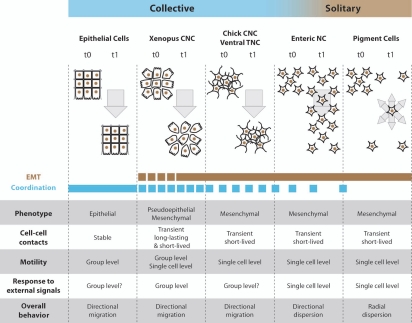
Figure 4.
Neural crest cells exhibit solitary and collective behaviors. Comparison between epithelial cells, cephalic, enteric and trunk NC cells. For each cell population their epithelial or mesenchymal phenotype and the type of cell-cell contacts are indicated. Motility at the group level means that non-motile cells can be pulled by adjacent motile cells while motility at the single cell level indicates that each cell is properly motile. Response to external signals at the group level means that the ability to respond to these signals depends on the fact that cells are part of a collective as opposed to a situation where each cell responds to external cues independently. Such collective guidance has been shown for Xenopus and mouse cephalic NC cells13,46 and is therefore likely to apply to other cephalic crests in other species. CNC, cephalic NC cells; TNC, trunk NC cells.