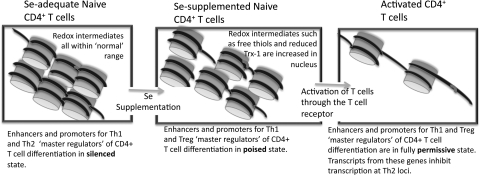
FIG. 12.
Hypothetical effect of higher Se intake on chromatin remodeling. Evidence suggests that higher levels of dietary Se may affect epigenetic states of certain gene regions, and this may be an important factor in how Se levels influences T helper cell differentiation. This may occur by increasing levels of redox intermediates in the nucleus such as free thiols on signaling molecules or reduced Txn-1, which may influence the rate-limiting steps of enzymes involved in chromatin remodeling. This can lead a poised state of chromatin that is able to more quickly respond to TCR-stimulation and rapidly generate mRNA for master regulator proteins such as T-bet. Txn-1, thioredoxin 1; T-bet, T-box expressed in T cells.