FIG. 15.
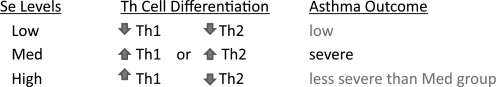
Results from mouse models of allergic asthma suggest that dietary Se levels may alter disease outcome. In relationship to the affects of dietary Se on T helper cell differentiation as outlined in Figure 10, low Se status leads to an overall lower immune response to Th2-inducing allergens. Increasing Se status to adequate levels increases TCR signal strength and enables stronger Th2 responses that drive allergic asthma. Further increasing Se status with Se supplementation further increases TCR signal strength, but skews CD4+ T cell away from Th2-type that drives allergic asthma.