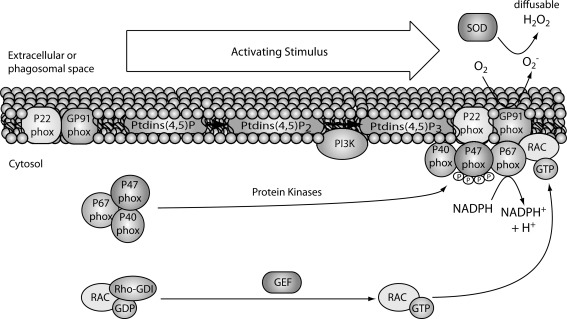
FIG. 4.
Generation of superoxide by NADPH oxidase. On activation (e.g., LPS in phagocytes or TCR in T cells), the cytosolic components including p47phox, p67phox, and p40phox, assemble at the membrane to form the enzyme complex. An electron is transferred through the catalytic core (b558) comprised of two subunits, gp91phox (NOX2) and p22 phox. In resting cells, GDP-bound RAC is in complex with its inhibitor GDI, and on activation, GTP is exchanged for GDP via guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) and this causes RAC to interact with membrane-associated p47phox. This GTP-bound form of RAC positively regulates the actions of the NOX2 complex, and the result is the transfer of one electron to oxygen to generate superoxide. This superoxide can subsequently be converted by SOD to diffusable H2O2. NADPH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; TCR, T cell receptor; PHOX, phagocytic oxidase; NOX, NADPH oxidase; RAC, Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate; GDI, GDP dissociation inhibitor; SOD, superoxide dismutase.