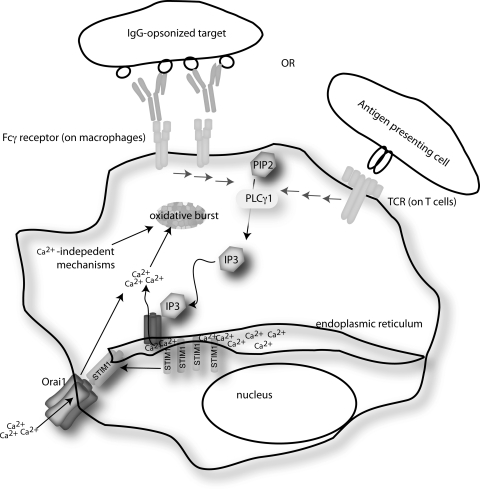
FIG. 6.
The basic steps involved in store-operated Ca2+ release (SOCE) for either T cells or macrophages. Stores of Ca2+ for these cells are largely maintained in ER. Engagement of receptors on the surface of immune cells leads to activation of PLCγ, which converts PIP3 to DAG and IP3. IP3 rapidly binds to the IP3 receptor on the ER membrane, which causes loss of Ca2+ from the ER stores. The lower [Ca2+] in the ER lumen is sensed by EF-hand motifs in the ER luminal STIM1 molecule, and this leads to oligomerization of STIM1. Oligomerized STIM1 physically interacts with Orai1 on the plasma membrane, which activates this channel and causes the entry of high levels of Ca2+. ER, endoplasmic reticulum; PLCγ, phospholipase Cγ; IP3; inositol-1,4, 5-trisphosphate; DAG, diacylglycerol; EF, elongation factor; STIM1, stromal interaction molecule 1.