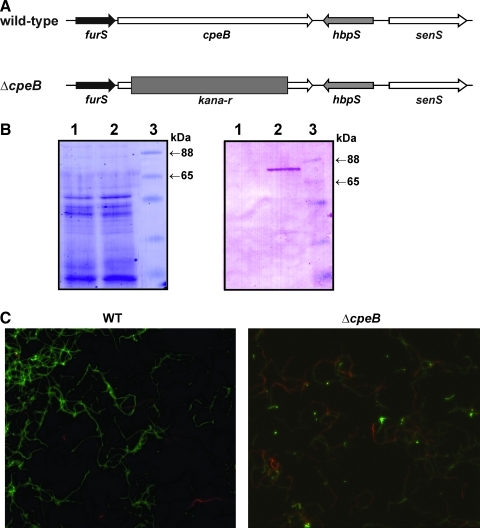
FIG. 6.
The Streptomyces reticuli ΔcpeB mutant. (A) Relative location of the genes furS, cpeB, hbpS, and senS within a DNA segment of the S. reticuli WT chromosome (WT, top). In the ΔcpeB mutant, the cpeB gene within the chromosomal DNA has been disrupted by the insertion of the kanamycin resistance (kana-r) cassette (ΔcpeB, bottom). (B) S. reticuli ΔcpeB (lane 1) and S. reticuli WT (lane 2) were cultivated in minimal medium containing 1% crystalline cellulose, as previously described (21). Proteins were released from the mycelium, subjected to 10% SDS-PAGE, and either stained with Coomassie (left) or transferred to a fluorotrans membrane for Western analysis by using anti-CpeB antibodies (right). The approximate sizes of two prestained protein markers are also indicated (lane 3). (C) S. reticuli WT and S. reticuli ΔcpeB (ΔcpeB) were cultivated in the presence of the redox-cycling compound plumbagin. Samples were subjected to a viability assay and subsequently examined by fluorescence microscopy. Living mycelia exhibit green fluorescence, whereas dead mycelia are seen in red. (To see this illustration in color, the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertonline.com/ars).