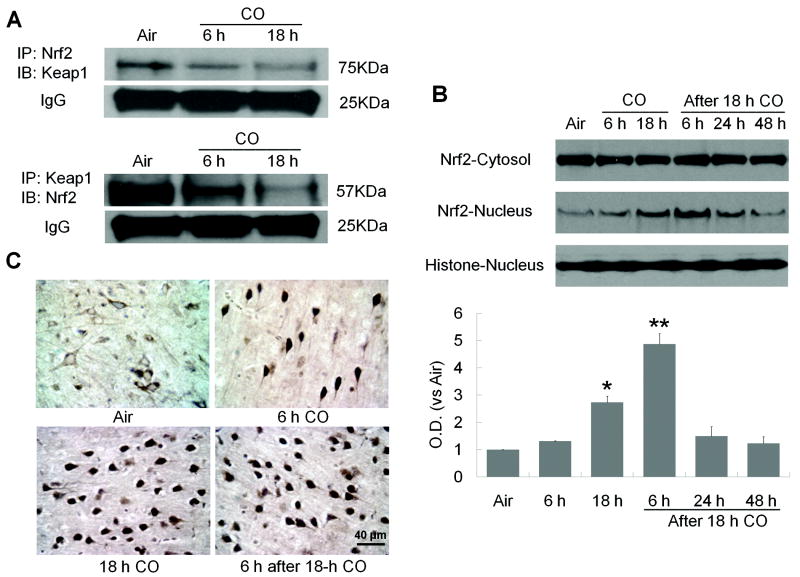
Figure 2.
CO increases Nrf2 nuclear translocation. (A) Nrf2 dissociates from Keap1 after 6- or 18-hour CO exposure. Immunoblotting showed that each antibody precipitated significantly less of the other protein after CO exposure, indicating a reduction in interaction between Nrf2 and Keap1. IgG was a protein-loading control. (B) Nrf2 protein expression was assessed in nuclear and cytosolic fractions at the times shown. Nrf2 expression was unchanged in the cytosolic fraction, but it was significantly increased in the nuclear fraction after 18-hour CO exposure and remained elevated for at least 6 hours after CO termination. Histone was used as a nuclear marker and as a protein-loading control. (C) Immunohistochemistry shows Nrf2 nuclear localization in the cortex of CO-exposed mice. In the air-treated group, most Nrf2 was cytoplasmic in cells with neuronal morphology. Nuclear staining of Nrf2 increased with increasing CO exposure time and remained high through 6 hours after CO exposure. The percentage of cells with nuclear Nrf2 staining was assessed on six non-overlapping fields for each section (n = 6 mice per group); *P<0.05, **P<0.01.