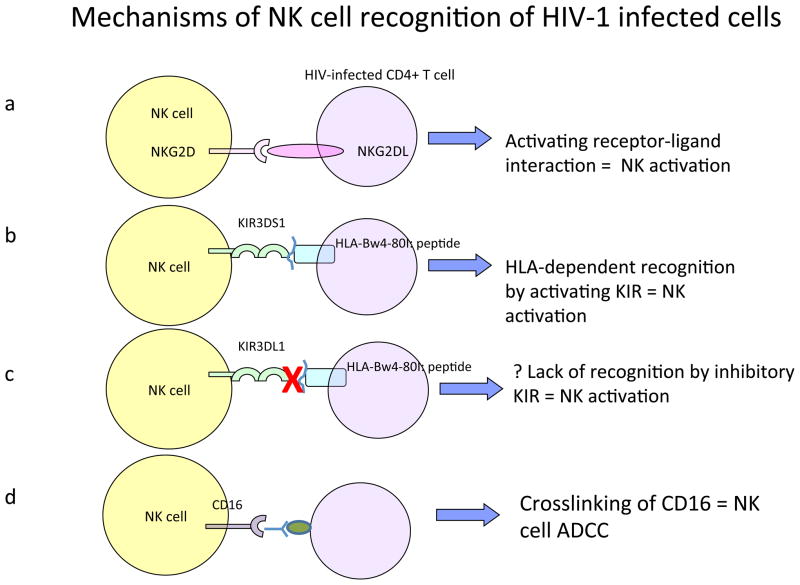
Figure 2. NK cell-mediated recognition of HIV-1-infected cells.
To date, it is not fully understood how natural killer (NK) cells recognize HIV-1-infected cells, and different mechanisms have been proposed. The expression of ligands for activating NK cells receptors on infected cells, such as NKG2D-ligands, results in the direct activation of NKG2D+ NK cells and target cell lysis (a). Changes in the epitopes presented by HLA class I molecules might allow for the engagement of activating killer inhibitory receptors (KIR) receptors, and resulting NK cell activation (b). Similarly, changes in HLA class I presented epitopes on HIV-1-infected cells can result in the disruption of the binding of inhibitory KIRs, leading to NK cell activation (c). Finally, antibodies binding to HIV-1-infected cells can crosslink CD16 and activate CD16+ NK cells (d).