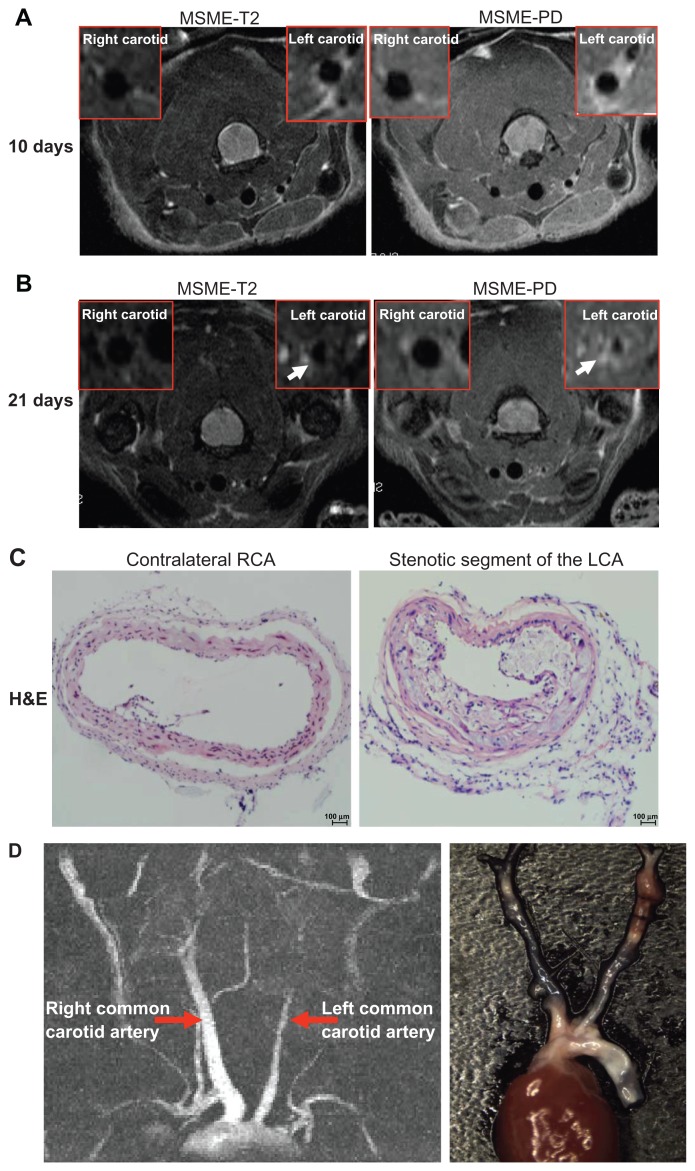
Figure 2.
Identification of neointima formation in apoE−/− mouse using in vivo MRI and the corresponding histology. (A) Example of MR images at day 10 following perivascular collar placement. MRI of a mouse with slight stenosis of the left carotid artery. The image shows an in vivo image of a transverse section at the RCA and LCA after perivascular collar placement using MSME proton-density/T2-weighted sequences. (B) Example of MR images at day 21 following perivascular collar placement. MRI of a mouse with significant stenosis of the left carotid artery. LCA with a neointima formation reveals a stenostic lumen, white arrows indicate aortic stenosis. (C) Corresponding H&E stain obtained in a mouse at 21 days following perivascular collar placement. Representative photomicrographs showing hematoxylin and eosin stained cross sections of proximal carotid site (H&E staining, 20×). (D) Representative carotid artery tree image in mice acquired at 7 T using 3D-FLASH sequence. The longitudinal view shows the characteristic stenosis of the left carotid artery.
Abbreviations: H&E, hematoxylin-and-eosin; LCA, left carotid artery; MR, magnetic resonance; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; MSME, multi-spin multi-echo; RCA, right carotid artery.