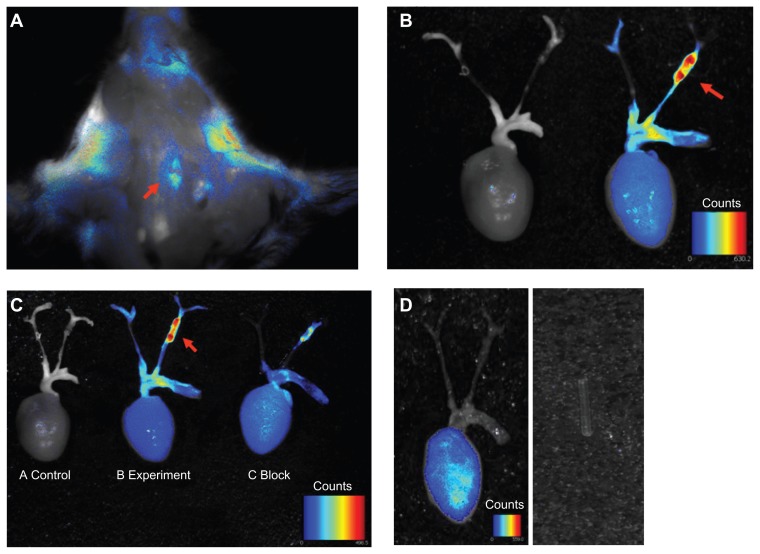
Figure 3.
Ex vivo overview of whole carotid artery imaging fluorescence c(RGDyK)-Cy5.5 signal. Pseudo-color fluorescence images of stenotic carotid artery mice were acquired 24 hours following intravenous injection of c(RGDyK)-Cy5.5. (A) In situ whole carotid artery imaging fluorescence c(RGDyK)-Cy5.5 signal, red arrow shows the region of interest of the stenotic segment of the left carotid artery. (B) Ex vivo whole carotid artery imaging fluorescence c(RGDyK)-Cy5.5 signal in a control mouse, and a mouse with a stenotic segment of the left carotid artery. (C) Ex vivo whole carotid artery imaging fluorescence c(RGDyK)-Cy5.5 signal in a control mouse, and a mouse with a stenotic segment of the left carotid artery, along with a mouse with a stenotic segment of the left carotid artery coinjections of 1 nmol of c(RGDyK)-Cy5.5 and bicyclic RGD peptide H-Glu[cyclo(Arg-Gly-Asp-D-Tyr-Lys)]2 using the Maestro in vivo imaging system. Red arrows indicate signal intensity. (D) Injection of Cy5.5 dye alone showed nonspecific binding. The PE tube itself gave no signal.
Abbreviation: PE, pressure equalization.