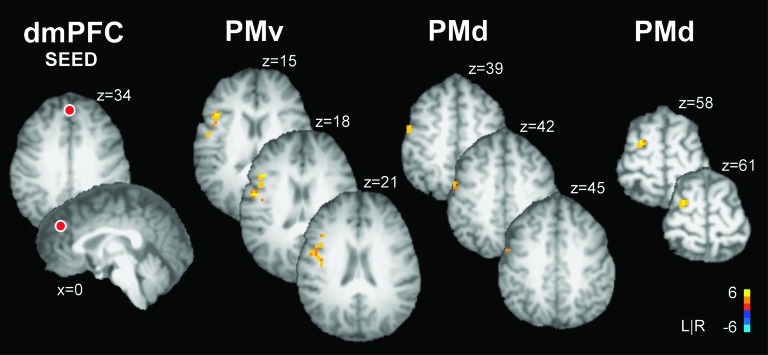
Figure 4.
Brain activity during the experimental task as revealed by the PPI functional connectivity analysis with the seed region placed in dmPFC. The location of the dmPFC seed is shown as a red sphere (not to scale) overlaid on an axial and sagittal slice of a single subjects transformed brain in Talairach space. The color bar ranges from t = −6 to t = +6 with a group activation threshold of P < 0.05, corrected. The corrected t-statistics associated with each voxel are displayed. PPI analysis revealed a task-dependent increase in functional coupling between activity in dmPFC and left PMv and dmPFC and left PMd. In each target region, activity is shown in a series of axial slices that are separated by 3 mm in the inferior to superior direction. When force production was paired with emotional as compared with neutral images, the BOLD signal increased in dmPFC and this increase was significantly coupled with increased activity in PMv and PMd. The findings suggest that a cortico-cortical network between motor and prefrontal regions regulates force control in emotional contexts.