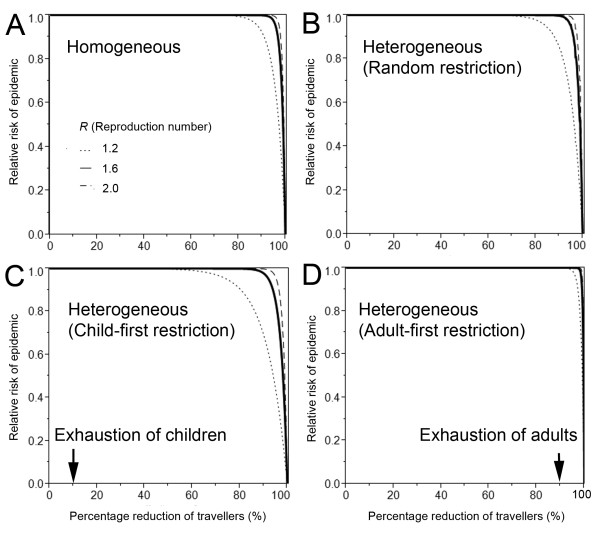
Figure 2.
Relative risk of epidemic by selective and non-selective travel restrictions. Relative risk of epidemic is shown as a function of the percentage reduction of travelers. In the absence of travel reduction, it is assumed that a total of 500 imported cases arrive in a virgin soil country. Three different reproduction numbers, 1.2 (dotted line), 1.6 (solid line) and 2.0 (dashed line) are considered. A. Non-selective travel restriction in a homogeneously mixing population. B. Non-selective travel restriction in a heterogeneously mixing population. C. Child-first restriction in heterogeneously mixing population. D. Adult-first restriction in heterogeneously mixing population. In C at 10% reduction of travel (specified with arrow), all travels involving children are restricted and the host to restrict travel is switched to adults. Similarly, adult travelers are exhausted at 90% reduction of travel in D.