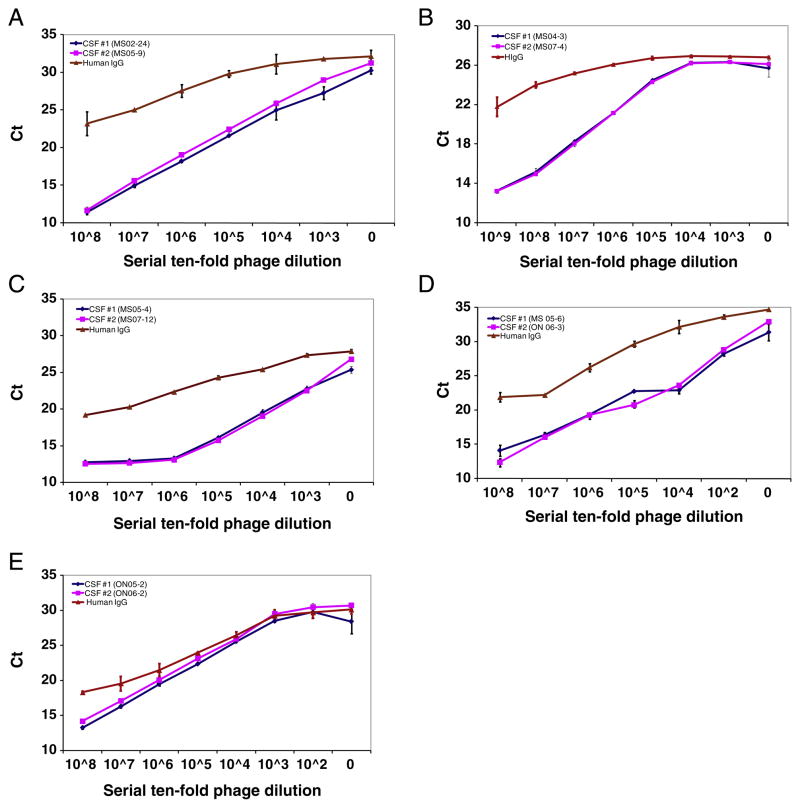
Fig. 1.
Dose-dependent phage-IPCR demonstrates peptide binding specificity to persistent IgG in the longitudinal CSF. Longitudinally obtained MS CSF and control pre-immune human IgG (50 μl at IgG concentration of 1 μl/ml) were coated in duplicate onto wells of protein A-plates before addition of the corresponding phage peptides (at serial 10-fold dilutions starting with 107 pfu) to each well. Bound phage were lysed and the DNA was amplified by real-time PCR. Peptide binding specificity was determined based on Ct values. Compared to control human IgG, phage peptides bound specifically to the paired CSF IgG with equal affinity in a dose-dependent manner. Experiments were repeated at least once. Error bars represent SD. A–E, Phage peptide binding specificity in patients 1–5, respectively. Data represent at least three independent experiments.