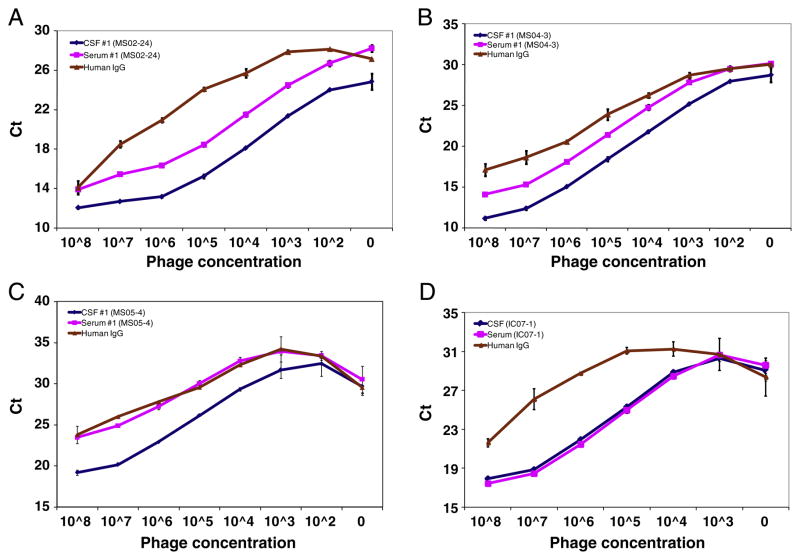
Fig. 4.
Targeting of intrathecally synthesized IgG by persistent phage peptides in dose-dependent phage-IPCR. Paired MS serum and CSF, as well as pre-immune human IgG control (50 μl at IgG concentration of 1 μl/ml), were coated in duplicate wells of protein A-plates before addition of the corresponding phage peptides (at serial 10-fold dilutions starting with 108 pfu) each well. Bound phage was determined by real-time PCR. Phage peptide bound at levels ~10-fold (3–4 Ct difference) higher to IgG in CSF than in serum in a dose-dependent manner. Preimmune human IgG served as negative control. Note that phage peptide selected by IC control IgG bound specifically to both serum and CSF IgG, indicating that it did not target intrathecal IgG. Experiments were repeated at least once. Error bars represent SD. A, patient 1 (02-24); B, patient 2 (04-3); C, patient 3; D, IC control patient (IC07-1, neurosyphilis). Data represent at least three independent experiments.