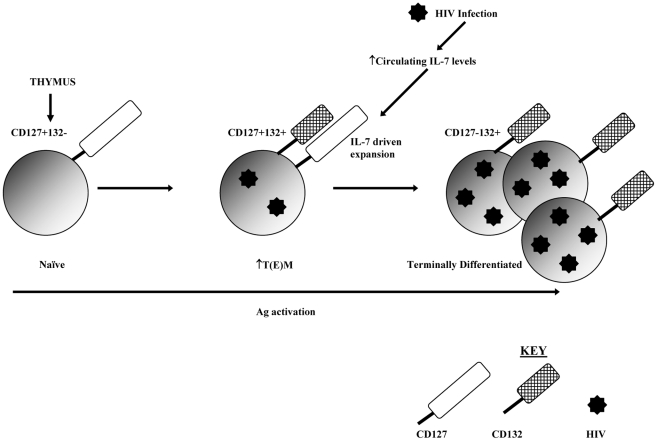
Figure 5. Proposed model for loss of CD127+132− and gain of CD127−132+ T-cells in HIV infection.
The data presented here suggest that T-cells exit the thymus expressing CD127 but not CD132. As these recent thymic emigrants mature through antigen (Ag) activation they co-express CD127 and CD132. The continuous antigenic activation and high circulating IL-7 levels associated with HIV infection results in ongoing activation and expansion of these CD127+132+ cells which progress to terminally differentiated CD127−132+ T-cell. As HIV preferentially infects activated cells these terminally differentiated CD127−132+ T-cells contain the greatest amount of viral DNA.