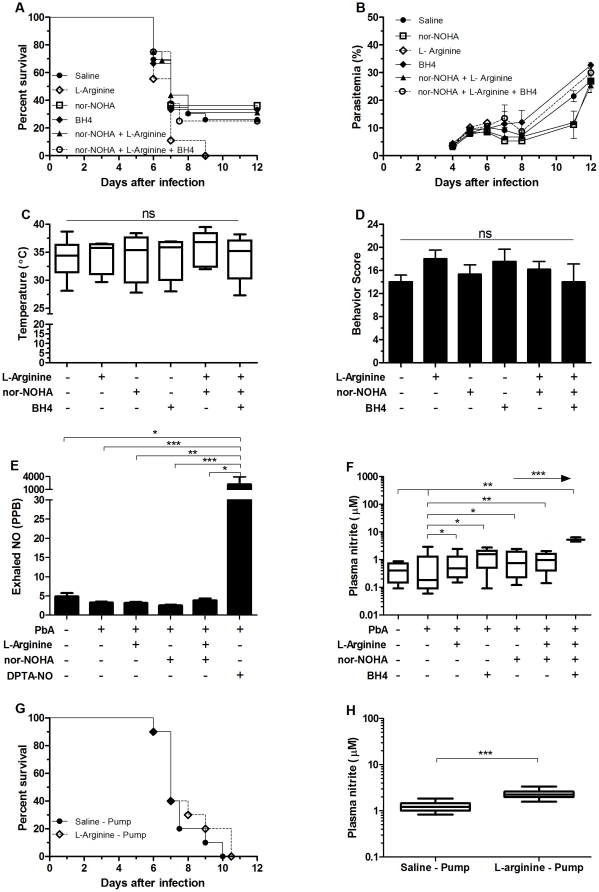
Figure 1. L-arginine and/or tetrahydro-L-Biopterin (BH4) supplementation combined or not with arginase inhibition did not prevent ECM.
Cumulative survival (A), course of parasitemia (B), rectal temperature (C), and motor behavior score (D) of PbA-infected mice treated with bolus injections of saline (n = 22), L-arginine 4 mg/mouse (n = 9), the arginase inhibitor Nω-hydroxy-nor-Arginine (nor-NOHA) 250 µg/mouse (n = 15), BH4 1 mg/mouse (n = 9), nor-NOHA+L-arginine (n = 16), and nor-NOHA+L-arginine+BH4 (n = 9). Rectal temperature and motor behavior score were measured on day 6 of infection. Exhaled NO (E) from selected groups was measured 1 hour after the morning treatment on day 5 of infection (n≥5 per group). Plasma nitrite (F) from selected groups treated with bolus injections. Cumulative survival (G) and plasma nitrite (H) of PbA-infected mice prophylactic treated with continuous L-arginine or saline supplementation using implanted osmotic pumps (n = 10 per group). Plasma nitrite (F, H) was measured on samples collected prior to the morning dosing on day 6 of infection (n≥5 per group). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, arrows indicate the presence of a linear trend.