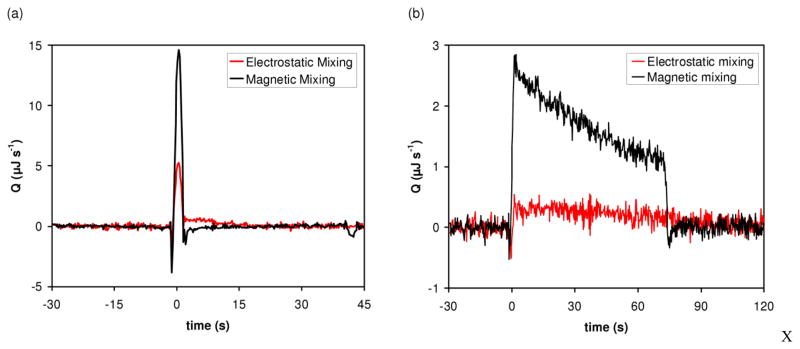
Fig. 4.
Comparison of thermal measurements using electrostatic mixing (i.e. mixing caused solely by the electrostatic merging of drops) and magnetic mixing. (a) Binding of BaCl2 to 18-crown-6 measured at 21°C in unbuffered water. The merged drops contained 2 mM BaCl2 and 2 mM 18-crown-6. (b) Enzymatic reaction. Trypsin hydrolysis of BAEE measured at 21°C in 200 mM Tris–HCl (pH 8.0), 50 mM CaCl2, and 0.2% polyethylene glycol (PEG) 8000. The merged drops contained 5 μM trypsin and 5 mM BAEE at the beginning of the reaction. Differential temperature as a function of time was converted to rate of heat generation (Q) as a function of time as described in Recht et al [21].