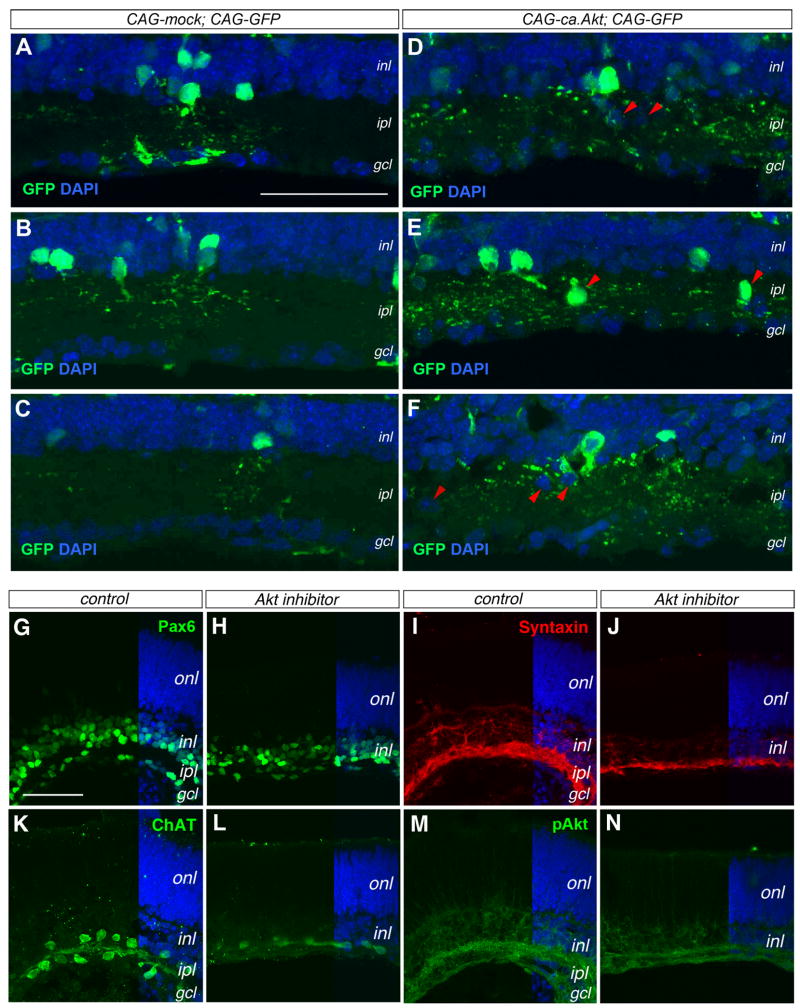
Figure 9. Akt activity affects amacrine cell morphogenesis and synaptic layer formation.
(A–F) Effects of constitutively active Akt by immunolabeling for GFP (merged confocal images 10 μm). P21 wild type retinas electroporated in vivo at P0 with control CAG-mock and CAG-GFP DNAs (A–C) or CAG-ca,Akt and CAG-GFP DNAs (D–E). Panels (A–C) and (D–F) contain similar numbers of GFP+ cells, but (D–F) show >3 fold more GFP+ dendritic labeling in the ipl. The red arrowheads in (D–F) point to ectopically localized cell somata.
(G–N) Impacts of Akt inhibitor on inner plexiform layer formation. Confocal images of P0 retinal explants cultured without (G, I, K, M) or with Akt inhibitor (H, J, L, N) for 8 days are immunolabeled for Pax6 (G, H), Syntaxin (I, J), ChAT (K, L), and pAkt (M, N). gcl, ganglion cell layer; inl, inner nuclear layer; ipl, inner plexiform layer; onl, outer nuclear layer. Scale bars, A for (A–F), G for (G–N), 50 μm.