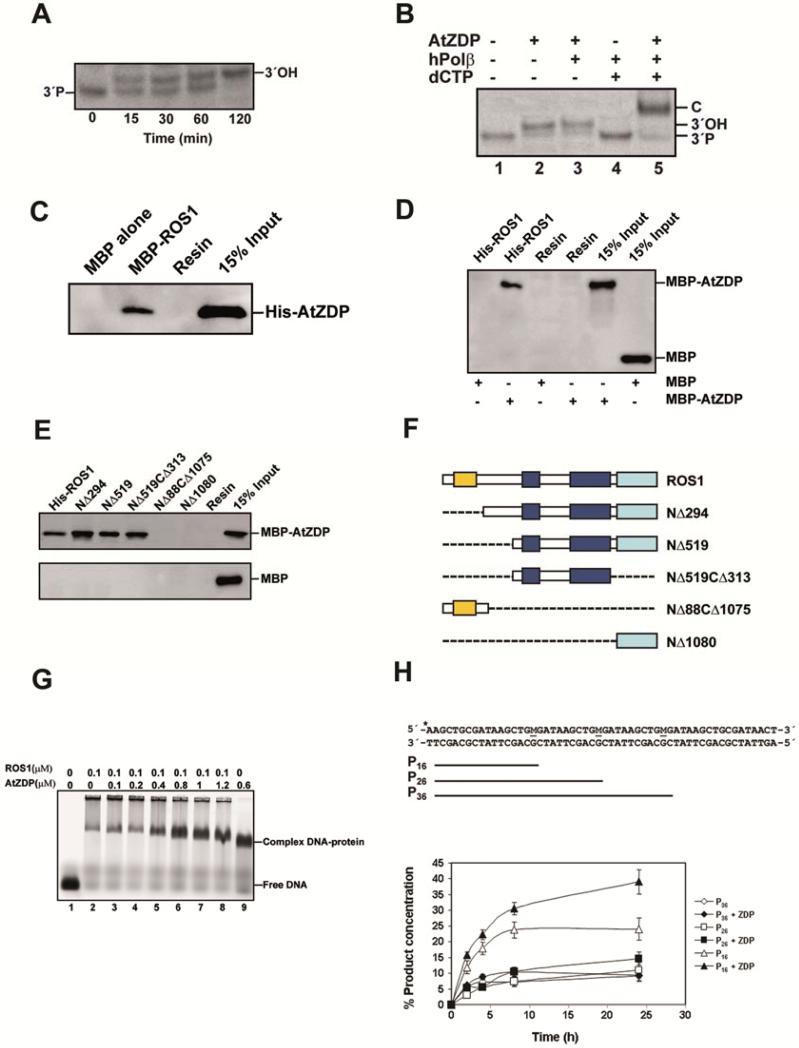
Figure 1. Characterization of ZDP biochemical activity and interaction with ROS1.
(A) Purified ROS1 (37.5 nM) was incubated at 30°C for 16 h with a double-stranded oligonucleotide substrate (40 nM) containing a 5-meC:G pair (See Table S1 for the sequence of the substrates). Reaction products were incubated with purified ZDP (1.5 nM) at 30°C. Reactions were stopped at the indicated times, products were separated in a 15% denaturing polyacrylamide gel and visualized by fluorescence scanning. (B) Reaction products of ROS1 were incubated with purified ZDP (6 nM) and human DNA polymerase β (hPol β, 0.5 U) during 30 min at 37°C, in the absence (lane 3) or presence (lane 5) of dCTP (0.2 mM). Lane 1: 3′-phosphate (3′P) marker. Lane 2: control reaction without hPol β. Lane 4: control reaction without ZDP. (C) Maltose Binding Protein (MBP) either alone or fused to ROS1 full-length (MBP-ROS1) was expressed in E. coli and fixed to an amylose resin. His-tagged ZDP purified from E.coli (His-ZDP) was incubated with either MBP-ROS1 or MBP bound to the resin. After washes, the proteins associated to the resin were separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred to a membrane and immunoblotted with antibodies against His6- tag. (D and E) Purified full-length ROS1 (FL-ROS1) or truncated ROS1 polypeptides fused to His6 -tag were fixed to a Ni-Sepharose column. The proteins bound to the column were incubated in the presence of either MBP-ZDP or MBP alone. After washes, the proteins associated to the resin were separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred to a membrane and immunoblotted with antibodies against MBP. (F) Schematic diagrams of full-length ROS1 and the different truncated ROS1 derivatives used in (E): lysine-rich domain (yellow), DNA glycosylase domain (blue), and C-terminal domain (cyan). (G) EMSA. Full-length ROS1 (0.1 μM) and increasing concentrations of ZDP were incubated with a labeled DNA duplex containing a single-nucleotide gap flanked by 3′-P and 5′-P termini. After nondenaturing gel electrophoresis, protein-DNA complexes were identified by their retarded mobility compared with that of free DNA, as indicated. See Figure S1 for the proteins used in pull-down assay. (H) Effect of ZDP on ROS1 processivity. Purified ROS1 (18 nM) was incubated with a double-stranded oligonucleotide substrate (40 nM) containing three 5-meC:G pairs (M, upper panel) in the absence (open symbols) or presence (closed symbols) of purified ZDP (144 nM) (lowe panel). Reactions were stopped at the indicated times and products were separated in a 12% denaturing polyacrylamide gel. Product concentration was quantified by fluorescence scanning: 16 nt (triangles), 26 nt (squares) and 36 nt (diamonds). Mean values of product concentration with standard errors from three independent experiments were shown. Also see Figure S1 for purified proteins used in pull-down assay and effect of ZDP on ROS1 activity.