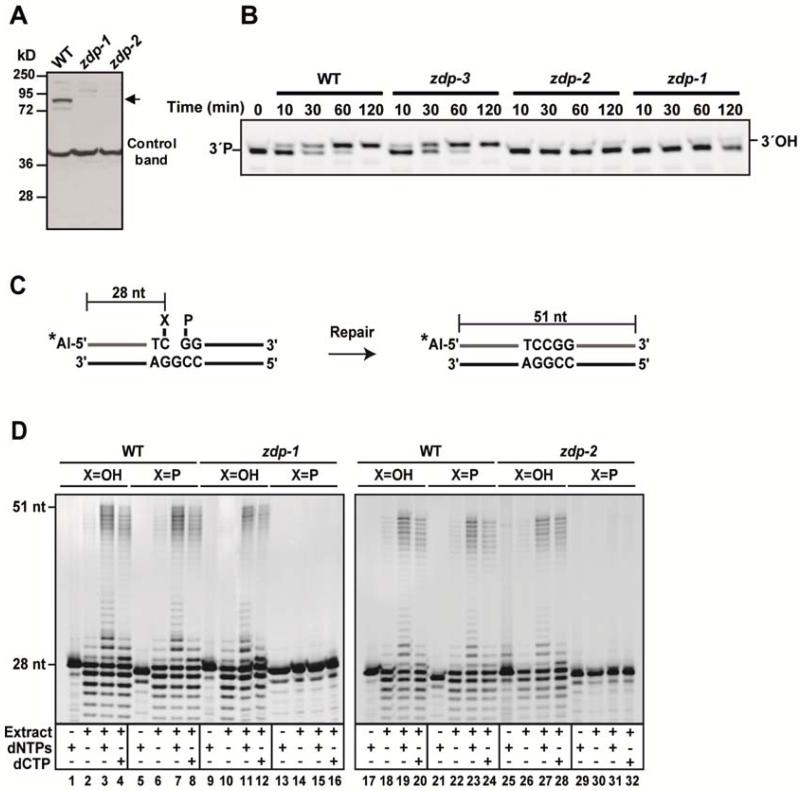
Figure 2. zdp mutant plants are unable to process DNA demethylation intermediates containing a gap flanked by 3′- and 5′-phosphate groups.
(A) Detection of ZDP protein levels in wild-type and mutant plants by Western blotting using an antibody against ZDP. A prominent non-specific band from the Western blot serves as a control for loading. Arrow points to the position of ZDP protein. (B) A DNA duplex containing a single-nucleotide gap flanked by 3′-P and 5′-P termini was incubated at 30°C with cell extracts from wild-type and zdp mutants. Reactions were stopped at the indicated times, products were separated in a 15% denaturing polyacrylamide gel and visualized by fluorescence scanning. (C) Schematic diagram of molecules used as DNA substrates in the repair assay. Double-stranded oligonucleotides contained a single-nucleotide gapped flanked by either a 3′P (X= P) or 3′OH (X= OH). The Alexa Fluor-labeled 5′-end of the upper strand is indicated by a star. The size of the fully repaired product is indicated. (D) DNA substrates were incubated with extract (45 μg protein) from wild-type (lanes 1-8 and 17-24), zdp-1-/- (lanes 9-16) or zdp-2-/- (lanes 25-32) mutant plants at 30°C for 2 h in a reaction mixture containing either dCTP or all four dNTPs, as indicated. Reaction products were separated in a 12% denaturing polyacrylamide gel, and detected by fluorescence scanning. Also see Figure S2 and Figure S3 for detailed T-DNA insertion mutants’ information.