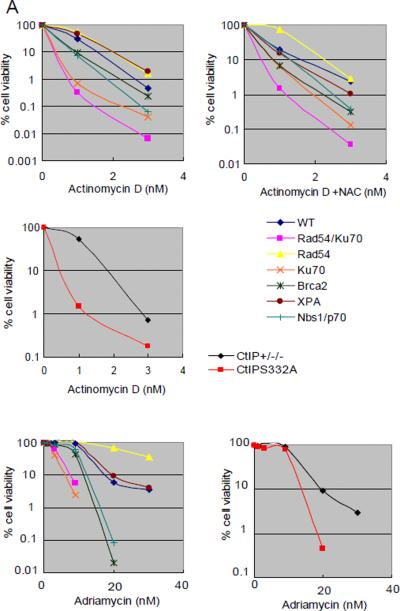
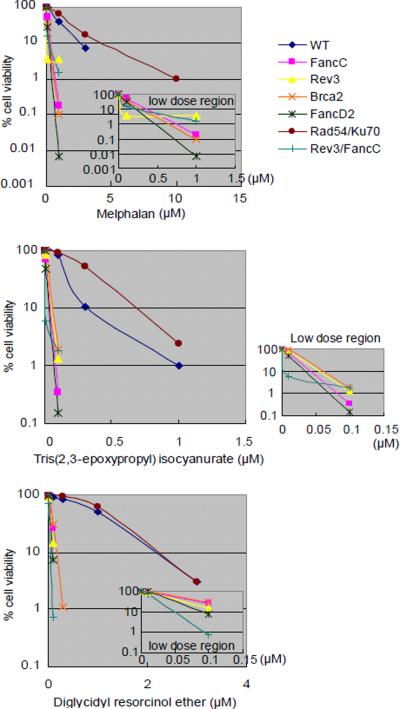
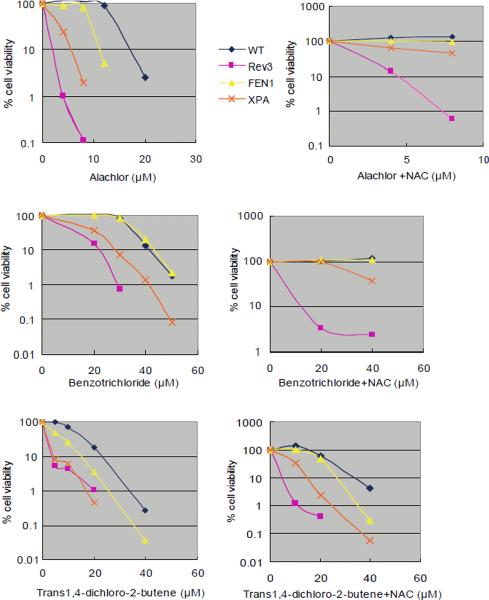
Figure 2.
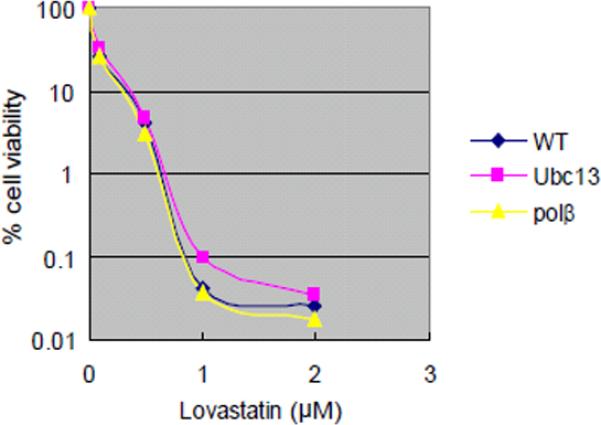
Sensitivity of DT40 isogenic DNA repair-deficient cell lines and the parental DNA repair-proficient cell line to chemical compounds.
Analysis of cell number by measuring levels of cellular ATP after a 72-hr exposure to actinomycin D and adriamycin (A); melphalan, diglycidyl resorcinol ether, tris(2,3-epoxypropyl)isocyanurate (B); alachlor, benzotrichloride, and trans-1,4-dichloro-2-butene (C); and lovastatin (D); (A–C) actinomycin D, alachlor, benzotrichloride, and trans-1,4-dichloro-2-butene were treated with or without antioxidant (1 mM N-acetyl-L-cysteine [NAC]). CtIPS332A cells are compared with CtIP+/−/− control cells (A).
The concentrations of each compound are displayed on the x-axis in a linear scale, whereas the corresponding extent of cytotoxicity (presented as % cell viability) is displayed on the y-axis in a logarithmic scale. On this log scale, the standard deviations for the data are within the symbol for each data point and are excluded for ease of viewing.