Table 1.
Enhancement of Oxime Elicited Rates of Reactivation of the SP- Methylphosphonyl Conjugates of Mouse Acetylcholinesterase with Various Mutations.1
| kr (mutant) / kr (wild type) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxime | Mutant |  |
 |
 |
| HI-62 | F295L | 20 | 12 | 2.5 |
| F297I | 2.9 | 3.1 | 1.8 | |
| Y337A | 18 | 12 | 0.18 | |
| F295L/Y337A | 118 | 13 | 0.55 | |
| F297I/Y337A | 21 | 7.1 | 1.8 | |
| Y337A/F338A | 0.91 | 0.46 | 0.13 | |
|
| ||||
| 2-PAM3 | F295L | 2.1 | 6.1 | 0.11 |
| F297I | 14 | 167 | 0.72 | |
| Y337A | 6.2 | 0.22 | 0.076 | |
| F295L/Y337A | 2.6 | 3.7 | 0.0032 | |
| F297I/Y337A | 11 | 1.5 | 0.49 | |
| Y337A/F338A | 0.71 | 2.3 | 0.043 | |
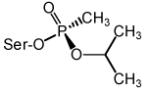
Data computed from Wong et al., 2000 and Kovarik et al., 2004. Structures of SP-cycloheptyl, 3,3-dimethylbutyl and isopropyl methylphosphonate conjugates with AChE are shown.
kr (wild type) was 122, 102 and 1330 min−1M−1 for SP-cycloheptyl, 3,3-dimethylbutyl and isopropyl methylphosphonate conjugates, respectively (Kovarik et al., 2004).
kr (wild type) was 0.66, 0.18 and 1080 min−1M−1 for SP-cycloheptyl, 3,3-dimethylbutyl and isopropyl methylphosphonate conjugates, respectively (Kovarik et al., 2004).
