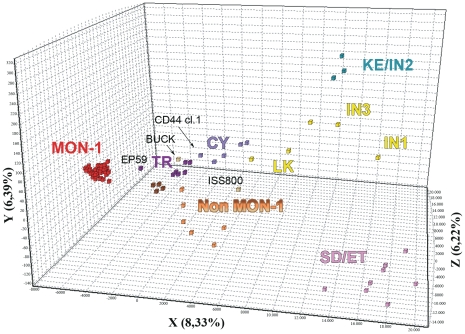
Figure 4. Factorial correspondence analysis (FCA) of the 76 L. donovani complex strains studied.
CY, Cyprus; ET, Ethiopia; GR, Greece; IN, India; KE, Kenya; LK, Sri Lanka; PT, Portugal; SD, Sudan; SP, Spain; TR, Turkey; Populations designated as MON-1 (red squares) and non MON-1 (orange and brown squares) include respectively L. infantum MON-1 strains from Greece, Turkey, Spain and Portugal and L. infantum non MON-1 strains from Spain, Portugal, France and Italy, corresponding to previous analyses [18], [21]; populations designated as IN1 (India 1), IN3 (India 3) and LK (Sri Lanka) (yellow squares); SD/ET (Sudan/Ethiopia) (pink squares); KE/IN2 (Kenya/India 2) (blue squares) compose the L. donovani genetic group, as detected previously [16], [17], [18], [21]; L. infantum non MON-1 strains from Turkey and Cyprus are designated as TR (dark purple squares) and CY (light purple squares), respectively. The MON-37 clone of CD44 strain from Cyprus groups with the other CY non MON-1 strains. The TR/CY strains are placed between the L. infantum MON-1 and non MON-1 populations and the hybrid strain EP59 from Turkey between the TR non MON-1 and MON-1 populations. The BUCK strain is placed very close to the TR non MON-1 strains, as previously described [18], [21].