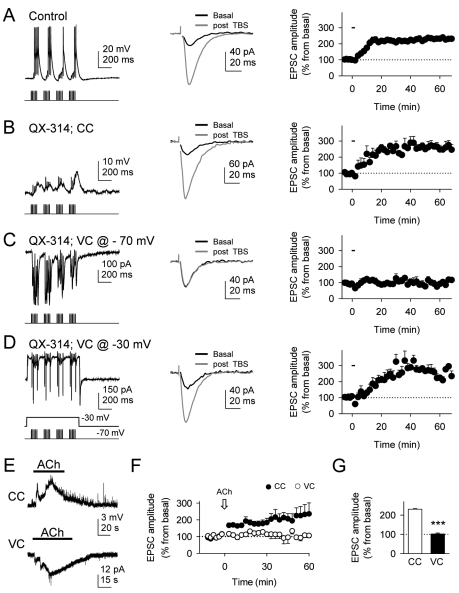
Figure 5. Cholinergic-induced hippocampal LTP depends on mild postsynaptic depolarizations.
(A) Left, CA1 pyramidal neuron response to a train of alveus TBS recorded in current-clamp conditions. Center, mean EPSCs (n = 10 consecutive EPSCs) before and 60 min after alveus TBS. Right, relative EPSC amplitudes versus time (n = 6). Zero time corresponds to the onset of alveus TBS that lasted 90.7 s (horizontal bar). (B, C, and D) as in (A), but in QX-314-loaded neuron recorded in current-clamp conditions (n = 7), in voltage-clamp conditions at a holding potential of −70 mV (n = 5) and −30 mV (n = 5), respectively. (E) Representative neuronal responses to application of ACh in current- (CC) and voltage-clamp (VC) conditions at a holding potential of −70 mV. (F) Relative EPSC amplitudes versus time in CC and VC before and after ACh application (arrow). (G) Average relative changes of EPSC amplitudes evoked 60 min after ACh application in CC and VC (n = 10 and 10, respectively). ***p<0.001.