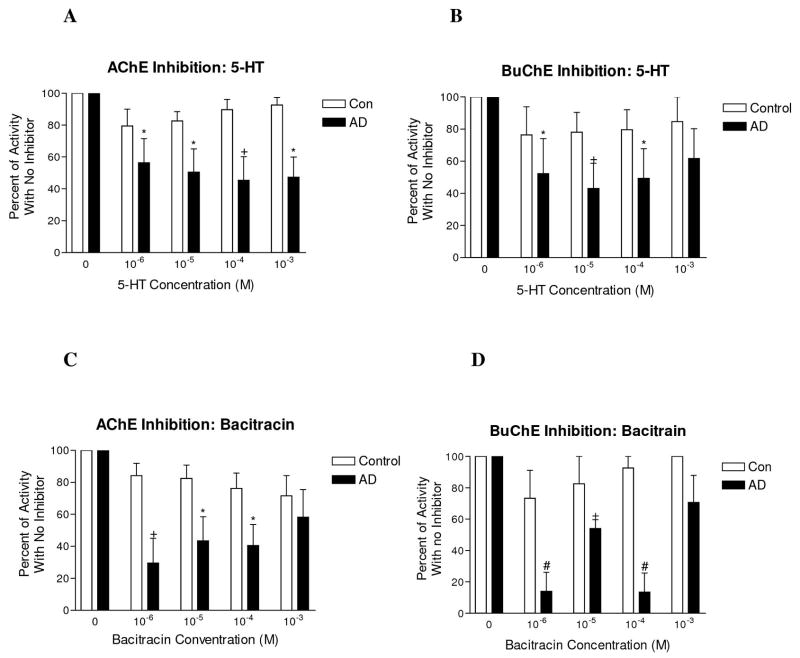
Figure 3.
Inhibition of AChE and BuChE activity in control and AD cortex by 5-HT and the protease inhibitor bacitracin. (A) In control temporal cortex, 5-HT resulted in inhibition of a negligible proportion of AChE when compared with no inhibitor condition. In contrast, 5-HT resulted in inhibition of a substantial proportion of AChE in AD temporal cortex. Inhibition in AD was significantly greater than the no inhibitor condition at every concentration of 5-HT used. (B) Similar to AChE, 5-HT resulted in inhibition of a negligible proportion of BuChE in control temporal cortex and a substantial proportion of BuChE in AD cortex. BuChE inhibition by 5-HT was significantly greater in AD when compared with no inhibitor condition for the three lower concentrations of 5-HT. (C) In control temporal cortex, bacitracin resulted in inhibition of a small proportion of AChE when compared with the no inhibitor condition. In AD, the proportion of AChE inhibited was substantially higher and was significantly greater than the no inhibitor condition for the three lowest concentrations used. (D) Similar to AChE, bacitracin inhibited a small proportion of BuChE in control frontal cortex and a substantially larger proportion in AD cortex which was significantly different than the no inhibitor condition for the three lowest concentrations used. Similar results were obtained in the frontal and temporal cortex. Trial experiments in the inferior parietal lobule (Brodmann area 40–41) displayed a similar pattern of inhibition as did trials using 5-HTP as inhibitor. * p<0.05, + p<001, # p<0.001.