Fig. 1.
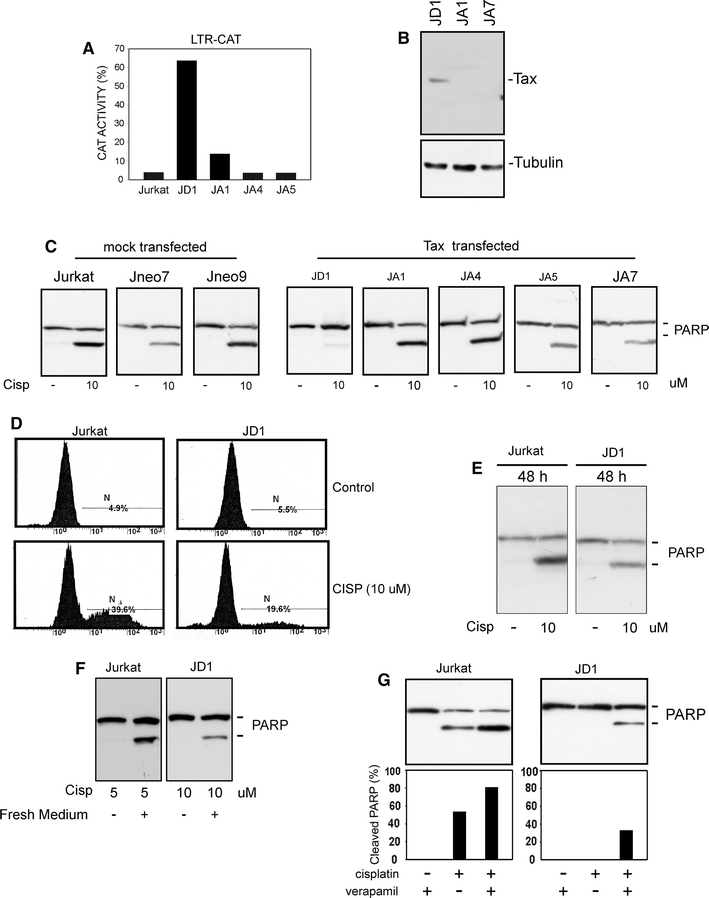
Phenotypic characterization of Jurkat-derived clones. a Analysis of Tax activity in Tax-transfected Jurkat derivatives. Cells were transiently transfected with an LTR-CAT plasmid; the β-galactosidase expression vector CMV-β-gal was added as a control of transfection efficiency. Percentage of chloramphenicol acetylation was calculated as described in “Materials and methods” and normalized for β-gal activity. b Western blot analysis of Tax expression in Jurkat cell derivatives; tubulin is shown as a loading control. c Western blot analysis of PARP cleavage after treatment with cisplatin for 24 h. Aliquots corresponding to 4 × 105 cells (or to 30 µg of total proteins) were subjected to SDS-PAGE, transferred to PVDF membranes and then immunodecorated with an anti-PARP antibody. d Annexin V cell death assay in Jurkat and JD1 cells treated with cisplatin for 24 h. e Western blot analysis of PARP cleavage in Jurkat and JD1 cells treated for 48 h with cisplatin. f Western blot analysis of cell death susceptibility of Jurkat and JD1 cells treated with cisplatin for 24 h and then growth for additional 24 h in cisplatin-free medium. g Analysis of the effect of cisplatin treatment in the presence of the MDR1 inhibitor verapamil. Cells were treated with cisplatin for 24 h in the presence of 20 µg/ml verapamil. At the end of treatment proteins were extracted as described in the “Materials and methods” and analyzed by Western blot. Histograms represent percentage of cleaved PARP, resulting from densitometric analysis
