Figure 4. Overlay of α-NRXN_2-6 with β-NRXN bound to NLGN-1.
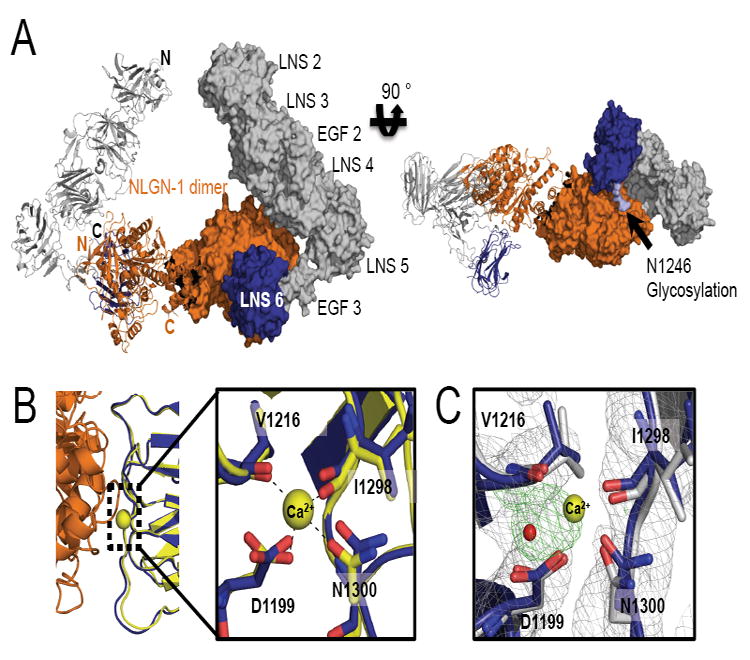
(A) A model of α-NRXN_2-6 in complex with the NLGN-1 dimer obtained by overlaying the LNS 6 domain in α-NRXN_2-6 onto the β-NRXN-1 molecules in the β-NRXN-1:NLGN-1 complex (PDB:3biw). The dimeric complex is shown as a ribbon representation for the left half and a surface representation for the right half. N- and C-termini are indicated on the left half in black for α-NRXN_2-6 and orange for NLGN-1. In the model, α-NRXN_2-6 can accommodate the NLGN molecule without steric hindrance, although with close proximity to LNS 4 (see also Supplemental Figure S3). The NLGN-1 dimer is displayed in orange and α-NRXN_2-6 is shown in gray (LN 2-EGF 3) and blue (LNS 6). On the right panel, a N-linked glycan on LNS 6 (N1246) is shown in light blue.
(B) The NLGN binding interface of α-NRXN_2-6 is conserved, as shown by the structural overlay with the NGLN-1:β-NRXN structure. In particular, the Ca2+-coordinating residues in β-NRXN (yellow) retain their conformation in the α-NRXN_2-6 LNS 6 domain (blue) despite the absence of Ca2+. Residue numbers are those of α-NRXN_2-6.
(C) An overlay of the Ca2+-free α-NRXN_2-6 molecule with Ca2+-bound β-NRXN-1 (PDB:3bod). The Ca2+ and water molecules in the β-NRXN structure are shown as yellow and red spheres, respectively. The 2Fo-Fc maps contoured at 1.2σ are displayed in gray and the Fo-Fc maps contoured at 3.0σ in green. In the absence of Ca2+, the LNS 6 domain in α-NRXN clearly coordinates an ion, which is likely to be sodium. Residue numbers are those of α-NRXN_2-6.
