Table 1.
Solvent and ligand effects on enantioselective decarboxylative allylation.a
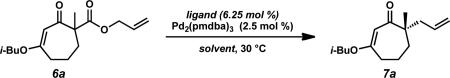 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry | ligand | solvent | yieldb(%) | eec(%) |
| 1 | L1 | THFe | 94 | 84 |
| 2 | L1 | 1,4-dioxane | 86 | 84 |
| 3 | L1 | 2-methyl THFe | 75 | 85 |
| 4 | L1 | TBMEe | 88 | 85 |
| 5 | L1 | Et2O | 93 | 86 |
| 6 | L1 | PhH | 84 | 86 |
| 7 | L1 | PhCH3 | 91 | 88 |
| 8d | L2 | PhCH3 | 57 | 90 |
| 9 | L3 | PhCH3 | 77 | 72 |
Conditions: β-ketoester 6a (1.0 equiv), Pd2(pmdba)3 (2.5 mol %), ligand (6.25 mol %) in solvent (0.1 M) at 30 °C; pmdba = 4,4’-methoxydibenzylideneacetone.
Isolated yield.
Determined by chiral HPLC.
Increased catalyst loadings were required to achieve full conversion: Pd2(pmdba)3 (5 mol %), L2 (12.5 mol %).
THF = tetrahydrofuran, TBME = tert-butyl methyl ether, 2-methyl THF = 2-methyl tetrahydrofuran.
