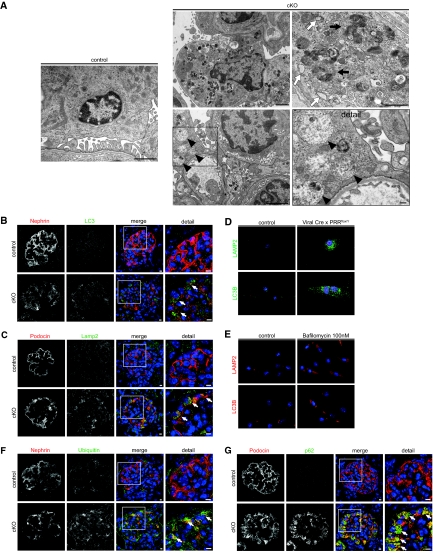
Figure 4.
Conditional PRR deletion (cKO) impairs autophagy and protein degradation by inhibiting vesicular acidification. (A) EM shows healthy podocytes and foot processes. EM of 14-d cKO mouse podocytes shows massive vacuolar accumulation with multivesicular bodies (black arrowheads), rough ER (white arrows), and lysosomes (black arrows). Immunofluorescence shows accumulation of (B) autophagy marker LC3B and (C) the lysosomal marker LAMP2 in cKO podocytes (arrows indicate positively stained podocytes). (D) In vitro, treatment of PRR floxed podocytes for 6 d with Cre recombinase adenoviral vector led to accumulation of LC3B- and LAMP2-positive structures; controls were treated with adenoviral LacZ (n = 3 independent experiments). Cre positivity was confirmed by costaining (red signal) with an appropriate antibody. (E) Similar results were obtained by treatment of murine podocytes with bafilomycin A1 or vehicle (DMSO) for 48 h at the indicated concentration. (F) Ubiquitin and (G) the autophagy adaptor protein p62 were strongly upregulated in cKO podocytes. Scale bars: 100nm (A, detail) 1 μM (A, any others); 5μm (B, C, F, G). Magnification: ×40 in D; ×20 in E.