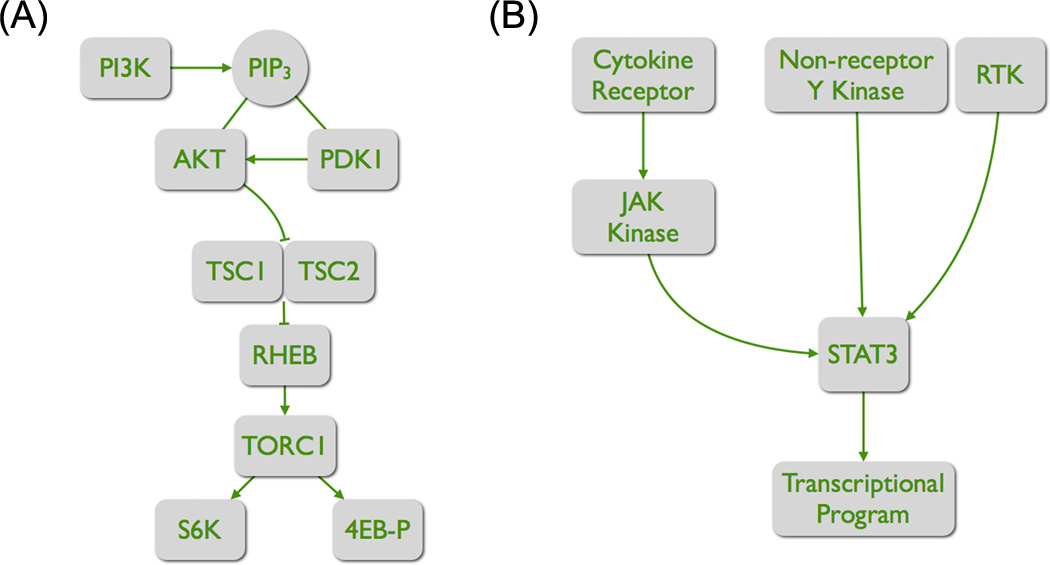
Figure 1. The core elements of two distinct signaling pathways.
(A) The PI3K-TORC1 pathway. The product of PI3K, PIP3, recruits the two serine-threonine kinases AKT and PDK1. PDK1 phosphorylates and thereby activates AKT. AKT has numerous targets. By phosphorylating TSC2, it inactivates the GTPase activity of the TSC complex. As a consequence, the GTP-bound form of the RAS-like protein RHEB increases, and RHEB activates TORC1. Important targets of TORC1 are S6K and 4EB-P. Phosphorylation of these targets increases the rate of protein synthesis.
(B) The activation of STAT3. Two principal routes lead to the phosphorylation and activation of STAT3. Binding of a cytokine to its cognate receptor leads to receptor dimerization and transphosphorylation of the associated JAK kinases. These kinases then phosphorylate STAT3. The phosphorylation results in dimerization, nuclear translocation and transcriptional regulator activity. Alternatively, STAT3 can be directly phosphorylated by RTKs and by non-receptor tyrosine kinases.