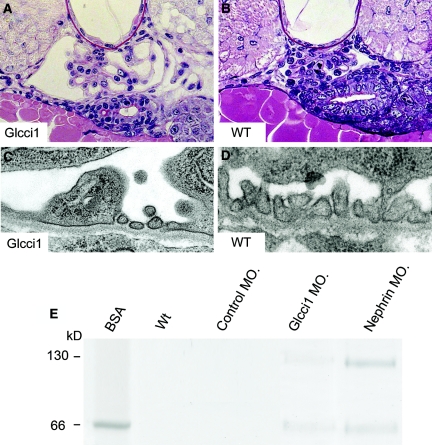
Figure 7.
Disruption of glcci1 expression causes abnormal glomerular capillary loops, podocyte effacement, and proteinuria. (A and B) In light microscopy, Periodic acid-Schiff staining shows dilated capillary loops and widened Bowman's space (A) compared with wild type (B). (C and D) In glcci1 knockdown embryos, the foot processes are largely lost because of effacement, but normal areas with intact slit membranes were also observed (C). Ultrastructural studies show normal podocyte foot processes, glomerular basement membrane, and endothelial cells in wild-type embryos (D). (E) Not only nephrin knockdown embryos but also glcci1 knockdown embryos develop proteinuria that can be observed by SDS-PAGE analysis. The main protein penetrating the filtration barrier was identified by mass spectrometry analysis as vitellogenin that has a size of about 150 and 70 kD, of the same size as BSA that primarily appears to be a degradation product of vitellogenin.