Abstract
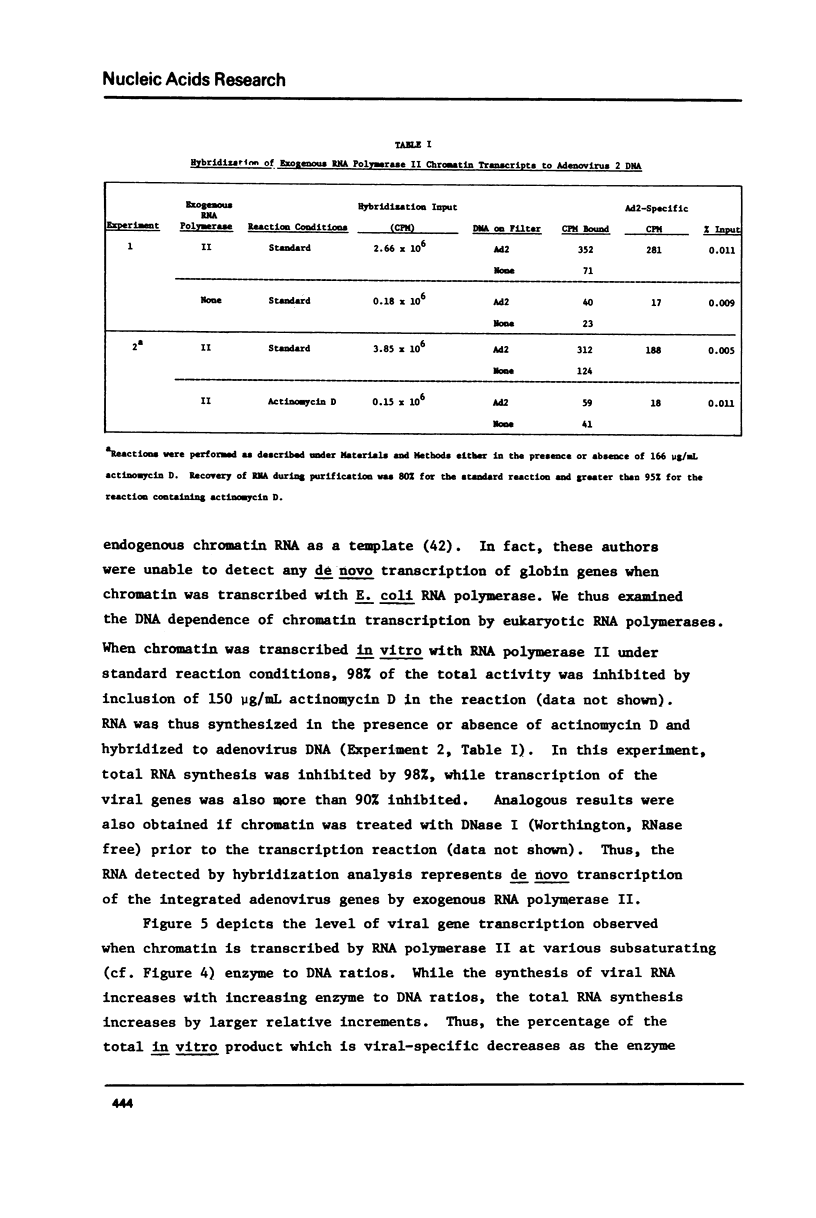
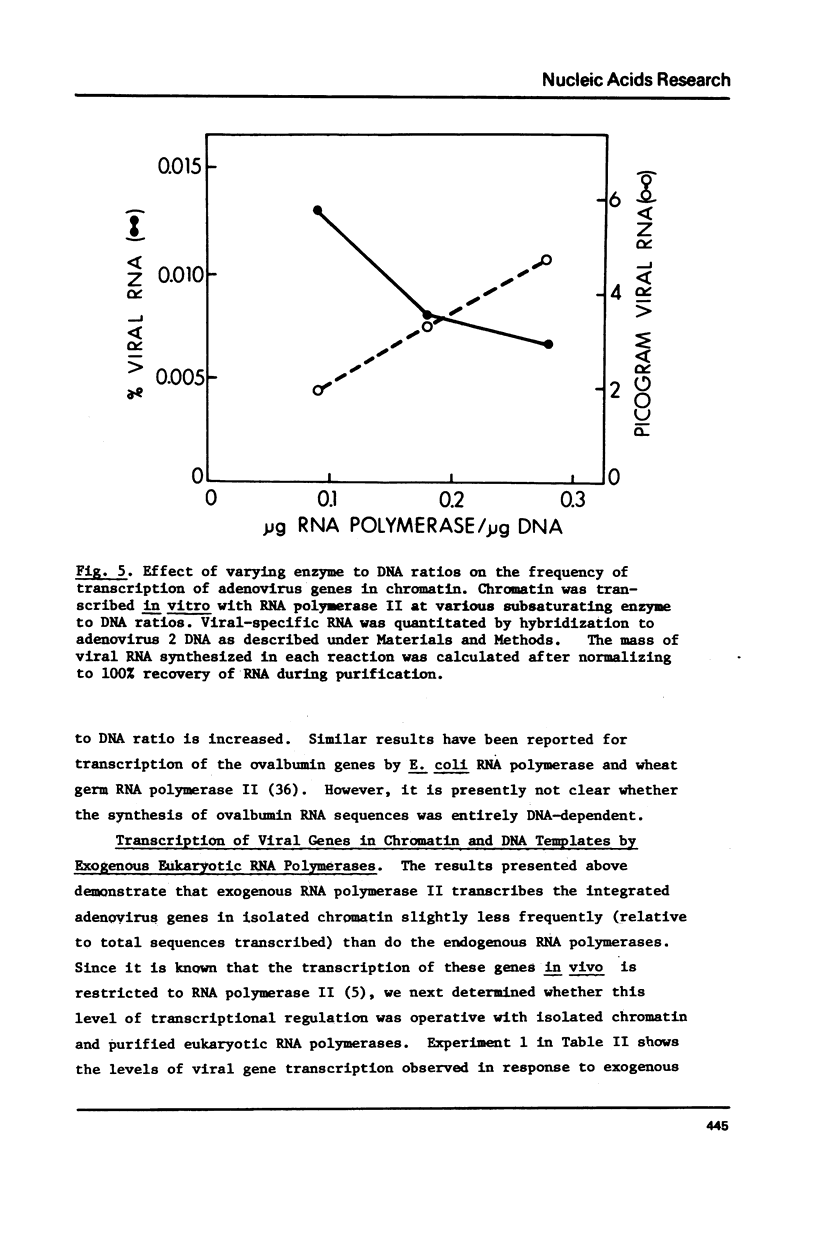
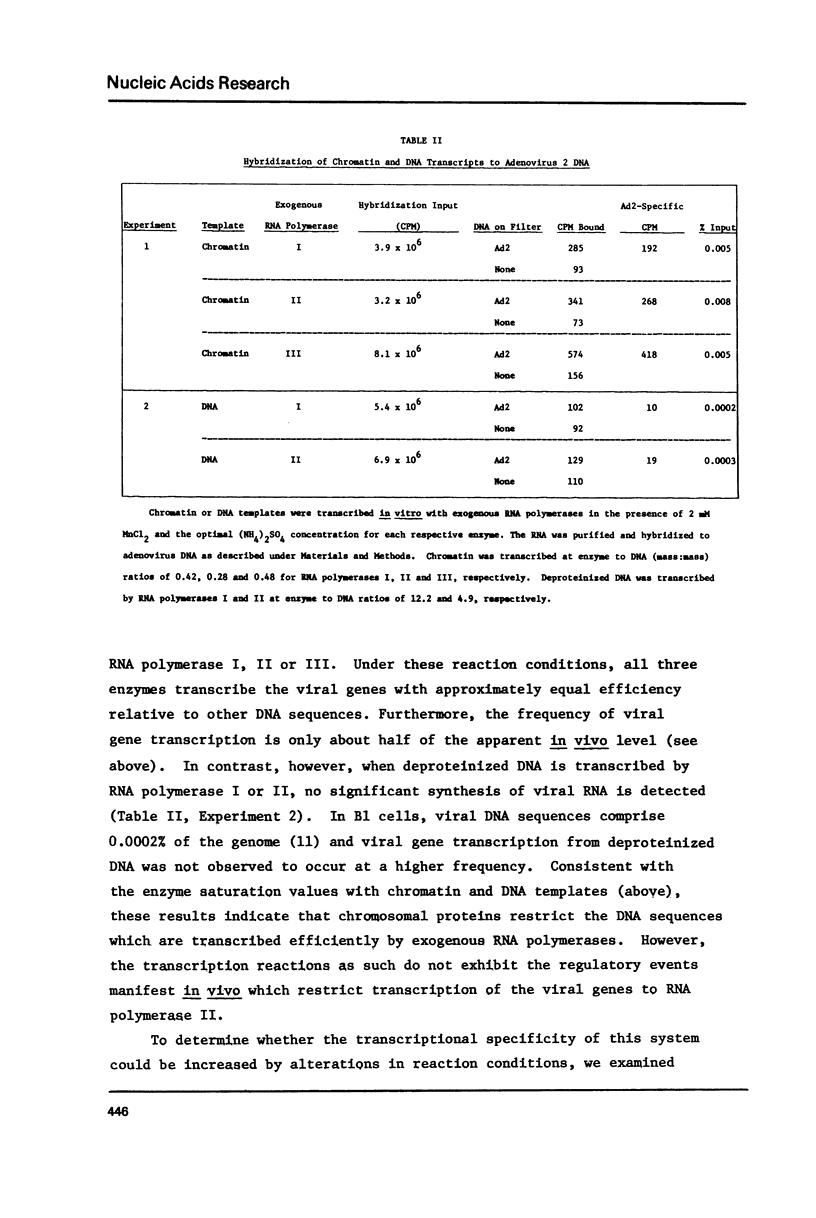
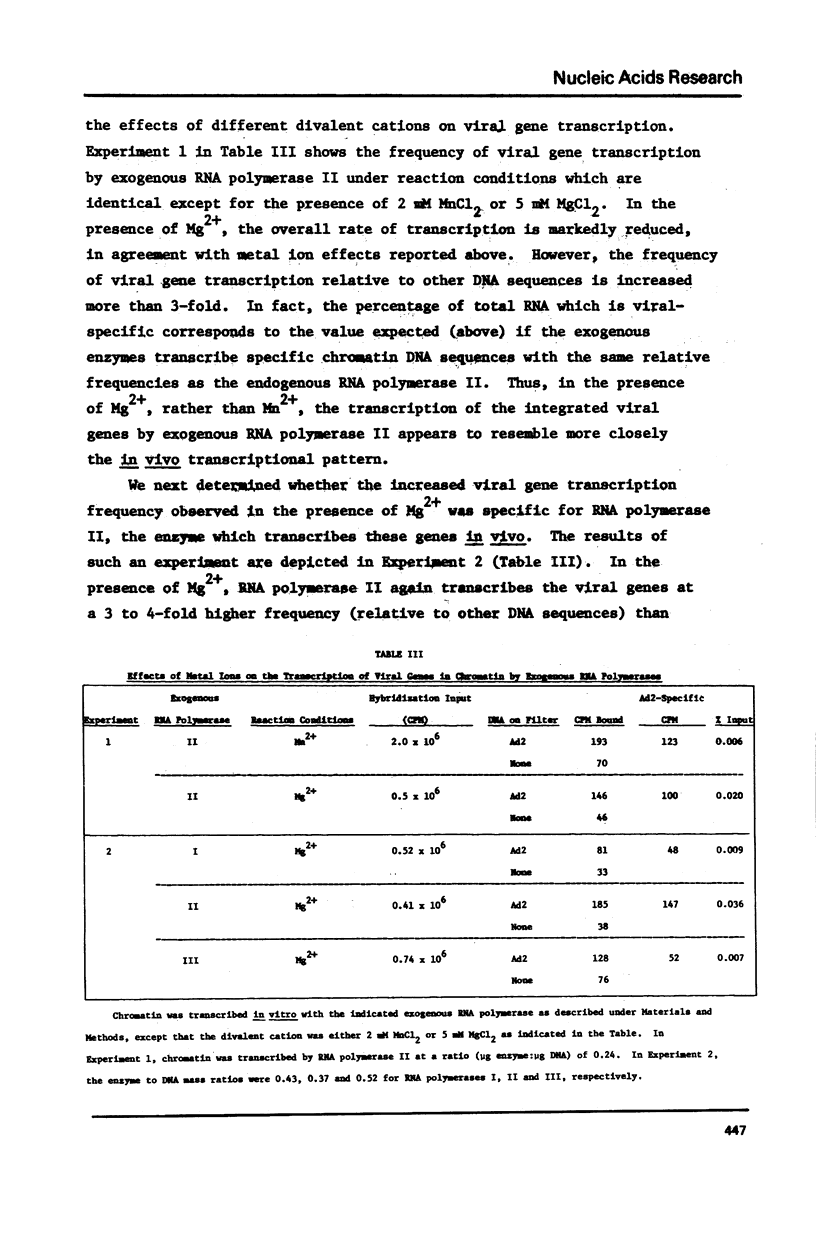
The transcription of chromatin from adenovrius 2 transformed rat cells by murine plasmacytoma RNA polymerases I, II and III has been studied. Both the total RNA synthesis and transcription of the integrated adenovirus 2 genes by RNA polymerase II represent de novo DNA transcription as assessed by their sensitivity to actinomycin D. It is shown that each RNA polymerase class has characteristic ionic strength activation profiles and metal ion requirements. RNA polymerase II transcribes the integrated adenovirus 2 genes in chromatin at a frequency 25- to 50-fold higher than their sequences are represented in the genome. In contrast, no detectable viral RNA is synthesized when deproteinized DNA is transcribed. In the presence of Mn2+, all three RNA polymerases (I, II and III) transcribe the integrated viral genes at approximately the same relative frequencey. However, the Mg2+ as divalent cation, the proportion of the total RNA which represents viral gene transcripts is increased 3- to 4-fold with RNA polymerase II, while it remains unchanged for RNA polymerases I or III.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axel R., Cedar H., Felsenfeld G. Synthesis of globin ribonucleic acid from duck-reticulocyte chromatin in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):2029–2032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.2029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biessmann H., Levy B., McCarthy B. J. In vitro transcription of heat-shock-specific RNA from chromatin of Drosophila melanogaster cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):759–763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitter G. A., Roeder R. G. Transcription of viral genes by RNA polymerase II in nuclei isolated from adenovirus 2 transformed cells. Biochemistry. 1978 May 30;17(11):2198–2205. doi: 10.1021/bi00604a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedar H., Felsenfeld G. Transcription of chromatin in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jun 25;77(2):237–254. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90334-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedar H. Transcription of DNA and chromatin with calf thymus RNA polymerase B in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jun 25;95(2):257–269. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90394-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambon P. Eukaryotic nuclear RNA polymerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:613–638. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.003145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A. Analysis of early adenovirus 2 RNA using Eco R-R1 viral DNA fragments. J Virol. 1975 May;15(5):1202–1213. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.5.1202-1213.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN M., PINA M. BIOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON ADENOVIRUS MULTIPLICATION, VI. PROPERTIES OF HIGHLY PURIFIED TUMORIGENIC HUMAN ADENOVIRUSES AND THEIR DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jun;51:1251–1259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.6.1251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallimore P. H. Viral DNA in transformed cells. II. A study of the sequences of adenovirus 2 DNA IN NINE LINES OF TRANSFORMED RAT CELLS USING SPECIFIC FRAGMENTS OF THE VIRAL GENOME;. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 15;89(1):49–72. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90162-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garel A., Axel R. Selective digestion of transcriptionally active ovalbumin genes from oviduct nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3966–3970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giesecke K., Sippel A. E., Nguyen-Huu M. C., Groner B., Hynes N. E., Wurtz T., Schütz G. A RNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity: implications for chromatin transcription experiments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Nov;4(11):3943–3958. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.11.3943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilboa E., Soreq H., Aviv H. Initiation of RNA synthesis in isolated nuclei. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jul 15;77(2):393–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11679.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour R. S., Paul J. Tissue-specific transcription of the globin gene in isolated chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3440–3442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gissinger F., Kedinger C., Chambon P. Animal DNA-dependent RNA polymerases. 10. General enzymatic properties of purified calf thymus RNA polymerases AI and B. Biochimie. 1974;56(3):319–333. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(74)80139-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris S. E., Schwartz R. J., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W., Roy A. K. Effect of estrogen on gene expression in the chick oviduct. In vitro transcription of the ovalbumin gene in chromatin. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 25;251(2):524–529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland M. J., Hager G. L., Rutter W. J. Transcription of yeast DNA by homologous RNA polymerases I and II: selective transcription of ribosomal genes by RNA polymerase I. Biochemistry. 1977 Jan 11;16(1):16–24. doi: 10.1021/bi00620a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquet M., Groner Y., Monroy G., Hurwitz J. The in vitro synthesis of avian myeloblastosis viral RNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3045–3049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaehning J. A., Roeder R. G. Transcription of specific adenovirus genes in isolated nuclei by exogenous RNA polymerases. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8753–8761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konkel D. A., Ingram V. M. Is there specific transcription from isolated chromatin? Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Apr;5(4):1237–1252. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.4.1237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Roeder R. G. Selective and accurate transcription of the Xenopus laevis 5S RNA genes in isolated chromatin by purified RNA polymerase III. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):44–48. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G. Multiple forms of deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase in Xenopus laevis. Isolation and partial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):241–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Roeder R. G. Purification and subunit structure of deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase I from the mouse myeloma, MOPC 315. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):5898–5906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Roeder R. G. Purification and subunit structure of deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase II from the mouse plasmacytoma, MOPC 315. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 10;250(9):3221–3228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Sklar V. E., Jaehning J. A., Weinmann R., Roeder R. G. Isolation and partial characterization of the multiple forms of deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase in the mouse myeloma, MOPC 315. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):5889–5897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih T. Y., Young H. A., Parks W. P., Scolnick E. M. In vitro transcription of Moloney leukemia virus genes in infected cell nuclei and chromatin: elongation of chromatin associated ribonucleic acid by Escherichia coli ribonucleic acid polymerase. Biochemistry. 1977 May 3;16(9):1795–1801. doi: 10.1021/bi00628a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T., Sober H. A. Circular dichroism of calf liver nucleohistone. Biochemistry. 1970 Aug 4;9(16):3103–3109. doi: 10.1021/bi00818a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklar V. E., Roeder R. G. Purification and subunit structure of deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase III from the mouse plasmacytoma, MOPC 315. J Biol Chem. 1976 Feb 25;251(4):1064–1073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklar V. E., Roeder R. G. Transcription of specific genes in isolated nuclei by exogenous RNA polymerases. Cell. 1977 Mar;10(3):405–414. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90028-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. M., Huang R. C. Transcription in vitro of immunoglobulin kappa light chain genes in isolated mouse myeloma nuclei and chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):775–779. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steggles A. W., Wilson G. N., Kantor J. A., Picciano D. J., Falvey A. K., Anderson W. F. Cell-free transcription of mammalian chromatin: transcription of globin messenger RNA sequences from bone-marrow chromatin with mammalian RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1219–1223. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein G., Park W., Thrall C., Mans R., Stein J. Regulation of cell cycle stage-specific transcription of histone genes from chromatin by non-histone chromosomal proteins. Nature. 1975 Oct 30;257(5529):764–767. doi: 10.1038/257764a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swetly P., Watanabe Y. Cell cycle dependent transcription of SV40 DNA in SV40-transformed cells. Biochemistry. 1974 Sep 24;13(20):4122–4126. doi: 10.1021/bi00717a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towle H. C., Tsai M. J., Tsai S. Y., O'Malley B. W. Effect of estrogen on gene expression in the chick oviduct. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 10;252(7):2396–2404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai M-J, Schwartz R. J., Tsai S. Y., O'Malley B. W. Effects of estrogen on gene expression in the chick oviduct. IV. Initiation of RNA synthesis on DNA and chromatin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 10;250(13):5165–5174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai M. J., Towle T. C., Harris S. E., O'Malley B. W. Effect of estrogen on gene expression in the chick oviduct. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):1960–1968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai M. J., Tsai S. Y., Towle H. C., O'Malley B. W. Effect of estrogen on gene expression in the chick oviduct. Studies on the initiation of RNA synthesis on chromatin in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 25;251(18):5565–5574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Groudine M. Chromosomal subunits in active genes have an altered conformation. Science. 1976 Sep 3;193(4256):848–856. doi: 10.1126/science.948749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto M., Jonas D., Seifart K. Transcription of ribosomal k-S RNA by RNA polymerase C in isolated chromatin from HeLa cells. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Oct 17;80(1):243–253. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11876.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasloff M., Felsenfeld G. Analysis of in vitro transcription of duck reticulocyte chromatin using mercury-substituted ribonucleoside triphosphates. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 15;16(23):5135–5145. doi: 10.1021/bi00642a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


