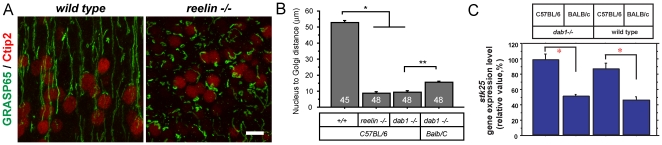
Figure 5. The Golgi extension and neuronal polarization phenotypes in dab1 mutant neurons is dependent upon mouse strain background.
The appearance of the Golgi apparatus was examined in 100 µm thick sections of the hippocampus at birth by immunostaining for GRASP65 and Ctip2 to identify pyramidal neurons. A In wild-type animals the Golgi apparatus extends several microns into the presumptive apical dendrite in the hippocampi, but in C57BL/6 dab1−/− mutants it is convoluted near the nucleus. The Golgi appears more elongated in the Balb/c dab1−/− mutant mice. Nucleus to Golgi distances were measured on isolated cells (insets). Arrowheads represent points used for measurements. B The nucleus to Golgi tip distances are greater for wild-type than dab1−/− mutants, and greater for BALB/c versus C57BL/6 dab1−/− mutants (*,** p<0.0001, Student's t test). C The number of multiple axon bearing neurons in dab1−/− mutant neurons is reduced on the BALB/c background as compared to the C57BL/6 background. In both cases, knocking down Stk25 leads to a further reduction in neurons with multiple axons and the development of neurons with no axons (* p<0.001 compared to the respective EV-control samples, ** p = 0.01 compared between EV-control samples, Student's t test) (Bar = 20 µm) Values for C57BL/6 samples have been published previously [34] and are shown here for comparison to BALB/c samples.