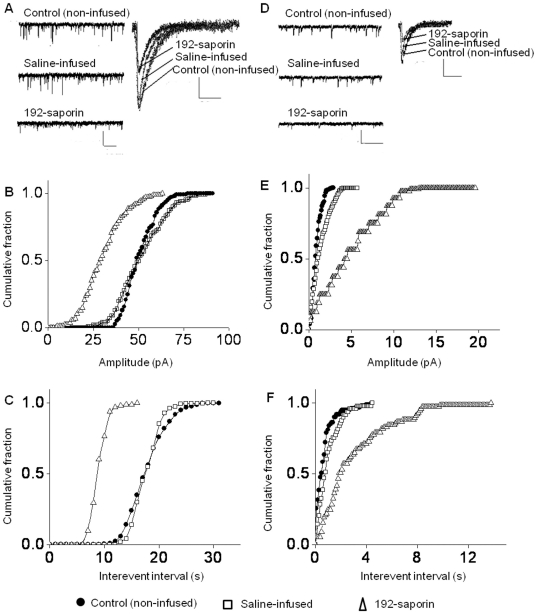
Figure 4. Inhibition of MS cholinergic pathway decreases the AMPA receptor activity in the CA1 pyramidal neurons of the hippocampus.
(A) Representatives of AMPA receptor mediated sEPSC traces in controls and 192-saporin infused rats recorded at −65 mV membrane potential; Calibration: 40 pA, 1 s. The adjacent average traces depict the reduction in the amplitude in the MS cholinergic lesioned rats compared to control rats, which show no difference in amplitude; Calibration: 15 pA, 30 ms. (B) Cumulative fraction plot of sEPSC amplitude from the composite data shows the shift of 192-saporin curve to the left from the controls, indicating reductions in amplitude. (C) Cumulative fraction plots of sEPSC interevent intervals exhibiting increased values for 192-saporin infused rats suggesting decreased frequency. (D) Representative traces of AMPA receptor mediated mEPSCs for the three groups (Calibration: 10 pA, 1 s) and the mEPSCs (Calibration: 10 pA, 30 ms) to show reduced amplitude in the 192-saporin infused rats. (E) Cumulative fraction plots for amplitude and (F) interevent interval exhibiting reduced amplitude and frequency.