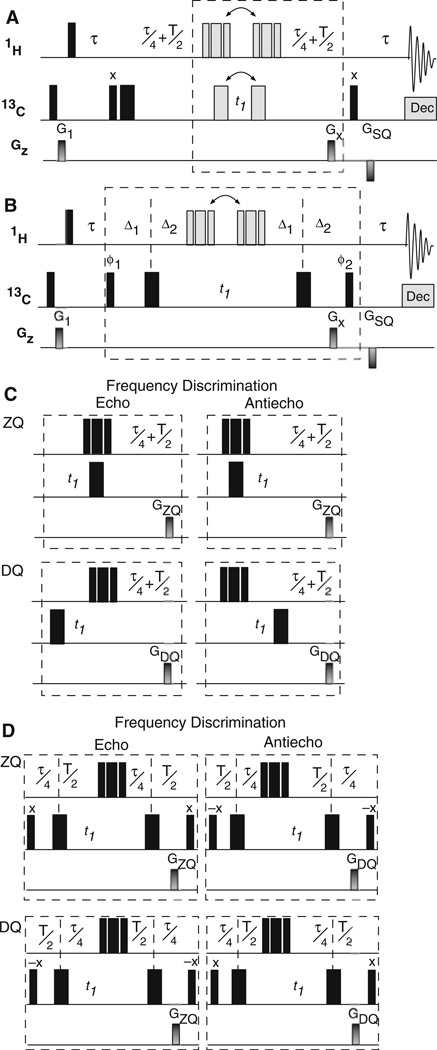
Fig. 3.
Hahn-echo gsHZQC pulse sequences for measurement of multiple-quantum transverse relaxation rates. a In the first half of the methyl multiplet filter, ZQ or DQ coherence is selected during the relaxation period (T) using a pulse sequence element shown in part C and similar to Fig. 2. b In the second half of the multiplet filter, the phase of the outer multiplet components is inverted using a pulse sequence element shown in part D. c A grid similar to that in Fig. 2 describes the evolution of magnetization through the pulse sequence in (a). In this case, the rows correspond to the multiple quantum coherence (ZQ or DQ) present during the relaxation delay and only one phase of the outer multiplet components is considered. The coherence selection (ZQ or DQ) during the relaxation delay is controlled by alternating the position of the 13C 180° before and after t1. Frequency discrimination is obtained by shifting the position of composite 1H (90x–180y–90x) pulse. d Inversion of the outer multiplet component in the pulse sequence in part B is achieved by shifting the two 13C 180° pulses between the relaxation delay (T/2) and the multiplet filter delay (τ/4). The relaxation delay (T) is equal to n/(2JCH) where n is any integer ≥1. Gradient strengths, phase cycles, and delays are as described in Fig. 1, except that the second 13C 90° pulse is used for the isotope filter. GSQ = (500 µs, 22.5 G/cm) in (a) and (b)