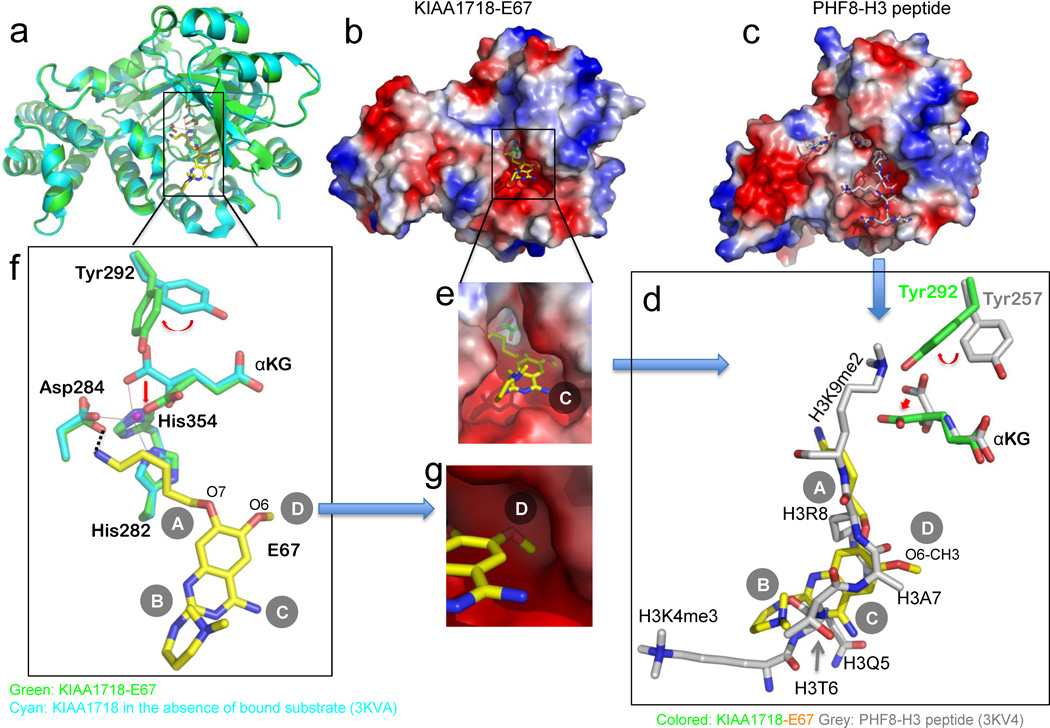
Fig. 2. Structure of KIAA1718-E67 complex.
(a) Superimposition of KIAA1718 Jumonji domain structures with bound E67 (colored in green) and in the absence of bound substrate (in cyan; PDB ID: 3KVA).
(b,c) Surface representation of the KIAA1718 Jumonji domain with E67 bound in the acidic substrate peptide binding groove (b), which is occupied by a histone peptide in the closely related PHF8 structure (c; PDB ID: 3KV4). The surface charge at neutral pH is displayed as red for negative, blue for positive, and white for neutral.
(d) Superimposition of H3 peptide (grey; taken from PDB ID: 3KV4) and E67 (yellow). The inhibitor occupies the space of bound histone H3 peptide from Lys4 (main chain) to Lys9 (main chain). The corresponding tyrosine (Tyr292 in KIAA1718 and Tyr257 in PHF8) adopts different rotamer conformation resulting in a different mode of binding of α-ketoglutarate (αKG).
(e) Enlarged view of E67 binding site with α-ketoglutarate (green) in the bottom of the pocket.
(f) Network of interactions centered on the amino group of 5-aminopentyloxy moiety at site A of E67. The metal ion (in small ball) is coordinated by side chains of His282, Asp284, His354 and two oxygen atoms of α-ketoglutarate.
(g) The methyl group of the O6 methoxy at site D of E67, mimics the side chain of histone H3 Ala7 (see panel d), is bound in a shallow surface pocket of KIAA1718.