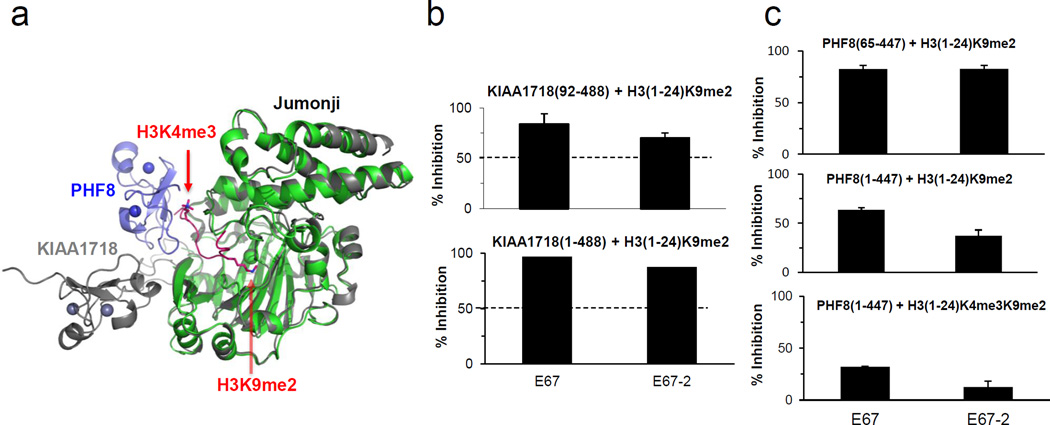
Fig. 3. Effect of PHD domain on the activity of Jumonji domain.
(a) Superimposition of KIAA1718 (PDB 3KV5; colored grey) and PHF8 (PDB 3KV4; colored blue for PHD and green for Jumonji) with a bound H3 peptide containing K4me3 and K9me2 (colored red).
(b) Percentage of inhibition for KIAA1718 (residues 1–488) (bottom panel) is comparable to those measured for the Jumonji domain only (residues 92–488) (top panel).
(c) Percentage of inhibition of the H3K9me2 demethylation activities of PHF8 Jumonji domain (residues 65–447) on H3(1-24)K9me2 (top panel), PHF8 (residues 1–447) on H3(1-24)K9me2 (middle panel), and PHF8 (residues 1–447) on the doubly methylated H3(1-24)K4me3K9me2 peptide substrate (bottom panel), under the conditions of 10 µM [I], 5 µM [S] and 2.5 µM [E] in 50 mM HEPES pH 7.0, 1 mM αKG, 50 µM Fe(NH4)2(SO4)2, and 2 mM ascorbic acid. For PHF8(1-447) activity on H3(1-24)K4me3K9me2 substrate (bottom panel), reaction mixtures were incubated for 10 minutes at 37 °C. For PHF8(1-447) and PHF8(65-447) on H3(1-24)K9me2 substrate, mixtures were incubated for 60 minutes at 37 °C. These time points were chosen to access the linear range of the product formation curve by these enzymes without completely exhausting the initial substrate.