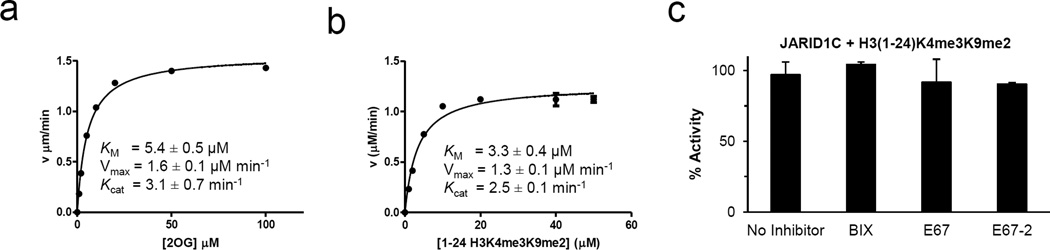
Fig. 4. Kinetic parameters and inhibition of JARID1C.
Michaelis-Menten plots of JARID1C (residues 1–839) for α-ketoglutarate (αKG) (a) and substrate H3 peptide (b). Initial velocity was plotted against αKG or peptide concentration and fitted with the Michaelis-Menten equation. Different concentrations of formaldehyde standards were made fresh and used to calibrate fluorescence intensities to determine initial velocities. The turnover number of FDH is fast enough to ensure the clearance of formaldehyde from JARID1C catalysis is not delayed by FDH conversion. Reactions were performed in 40 µl volume under the conditions of 20 µM H3(1-24)K4me3K9me2 [S], 0.5 µM JARID1C [E], 2 mM ascorbic acid, 1 mM αKG, 0.1 mM Fe(II), 20 mM MES pH 6.5, 50 mM NaCl, 0.6 mM APAD+ and 3 µM FDH at 37 °C for 10 min monitored by a BioTek Synergy™ 4 Hybrid Microplate Reader. All elements were pre-incubated at 37 °C for 15 min followed by addition of peptide and APAD+ to initiate the reaction. Experiments were done in triplicates and initial velocities were then plotted against peptide or α-KG (also know as 2-oxoglutarate or 2OG) concentrations and fit with the Michaelis-Menten equation using GraphPad Prism 5.0.
(c) H3K4me3 demethylation activity of JARID1C(1-839) on H3(1-24)K4me3K9me2 substrate, under the conditions of 0.25 µM enzyme [E], 10 µM peptide substrate [S] and 10 µM inhibitor [I] in 50 mM MES pH 6.8. Enzyme was pre-incubated with inhibitor at room temperature (~ 21 °C) prior to the addition of substrate peptide and the reactions were lasted for 10 min at 37 °C.