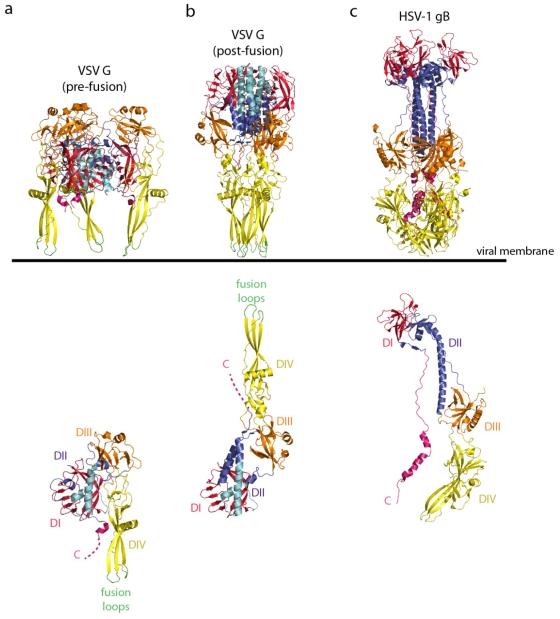
Figure 1.
(a) Ribbon diagrams of the vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) glycoprotein (G) pre-fusion trimer (top) and protomer (bottom) (PDB code = 2J6J [73]). (b) Ribbon diagram of the VSV G post-fusion trimer (top) and protomer (bottom) (PDB code = 2CMZ [72]). G is depicted by domains; the lateral domain (domain I) is in red, the pleckstrin homology domain (domain III) is in orange, and the fusion domain (domain IV) is in yellow. The trimerization domain is colored with two shades of blue (the part of G that retains its structure during refolding is in cyan, and the part of G that is refolded during the structural transition is in deep blue). The fusion loops are green and the C-terminus is pink. (c) Ribbon diagram of the HSV-1 gB trimer (top) and protomer (bottom) (PUB: 2GUM [74]). gB is colored by domains with the same color code as VSV G. The orientation of the VSV G and HSV-1 gB trimers toward the viral membrane is indicated. The VSV G protomers are aligned on the rigid block made of the lateral domain (in red) and the cyan part of the trimerization domain. The orientation of the post-fusion protomer is thus different in the top and the bottom of the figure.