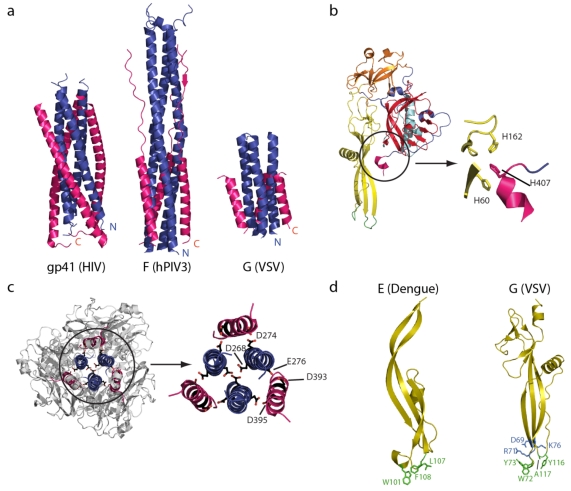
Figure 2.
(a) A comparison of the central six-helix bundle of the class I viral fusion proteins (HIV gp41 and hPIV3 F) and class III viral fusion proteins (VSV G) in their post‑fusion conformation. The amino-terminal trimeric coiled-coil is in blue and the antiparallel lateral helices are in pink. (b) A close up view of the histidine cluster located at the fusion domain/C-terminal domain interface that has to be disrupted during the structural transition from pre- to post fusion structure. (c) Top view and close up of the VSV G trimerization domain showing the clusters of acidic residues in the post-fusion state. (d) The structural organization of the Dengue virus E fusion domain (left) and the VSV G fusion domain (right). The hydrophobic residues in the tips of the fusion domains are depicted in green and, for VSV G, charged residues that impede deep penetration of the fusion domain inside the membrane are in blue.