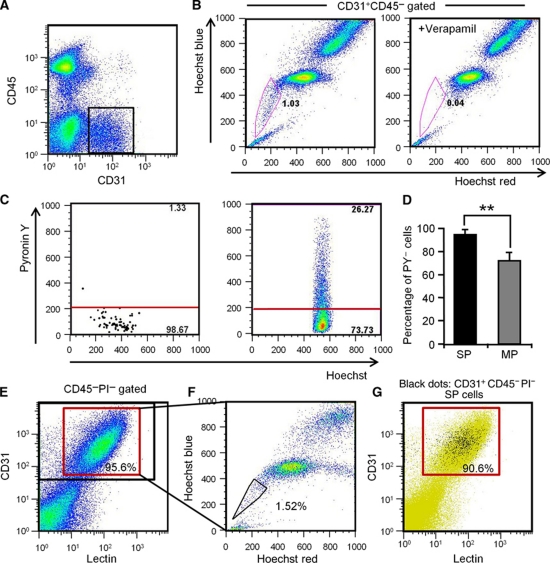
Figure 1.
Identification of endothelial side population cells. (A) Flow cytometric analysis of hind limb ECs from wild-type mice. (B) Hoechst 33342 staining of CD31+CD45− ECs gated as shown in (A). Note that verapamil selectively prevents Hoechst exclusion from EC-SP cells. (C) Incorporation of Pyronin Y (PY) in EC-SP (left-hand side) and EC-MP (right-hand side) cells. (D) Quantitative evaluation of PY− cells among EC-SP (SP) and EC-MP (MP) cells. Error bars are ±s.e.m. **P<0.01 (n=7). (E) Flow cytometric analysis of mouse hind limb ECs after in-vivo infusion of lectin. Lectin-positive cells among the CD31+CD45− cells are shown in the red gate and total CD31+CD45− cells are shown in the black gate. 95.9±0.2% (n=6) of the CD31+CD45− ECs were lectin positive. (F) Hoechst staining of lectin+ CD31+CD45− cells. (G) Representative flow cytometric plots of EC-SP cells (black dots). The lectin-positive population is shown in the red gate. 90.6±1.4% (n=4) of the EC-SP cells were lectin positive.