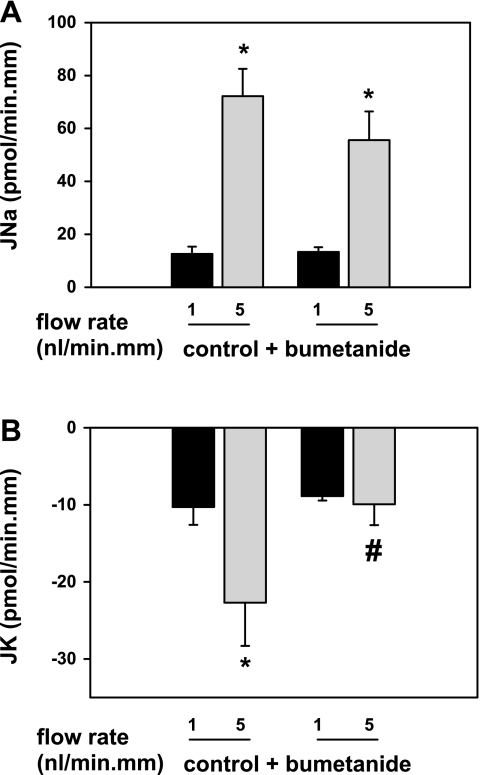
Fig. 1.
Effect of basolateral bumetanide (100 μM) on basal and flow-induced net cation transport (in pmol·min−1·mm−1) in isolated, perfused rabbit cortical collecting ducts (CCDs). In untreated CCDs (n = 4), an increase in tubular fluid flow rate from ∼1 (slow) to 5 (fast) nl·min−1·mm−1 was associated with a significant increase in Na absorption (JNa; A) and net K secretion (JK; B). Pretreatment of CCDs (n = 4) with 100 μM bumetanide added to the bath solution was without an effect on flow-stimulated JNa (A), but completely inhibited flow-induced K+ secretion (FIKS; B). These data provide compelling support for a critical role of a basolateral bumetanide-sensitive process in FIKS in the rabbit CCD. Means ± SE. *P < 0.05 compared with Jx at 1 nl·min−1·mm−1 in the same tubules. #P < 0.05 compared with Jx in control tubules studied at the same flow rate.